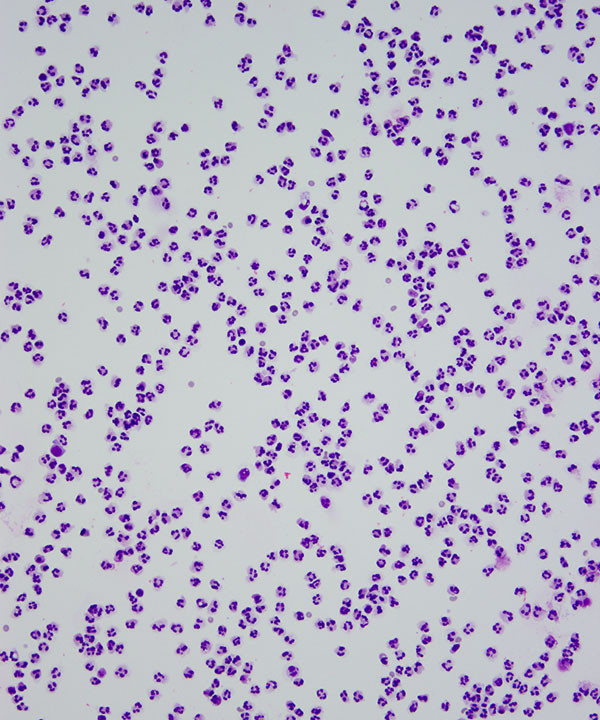
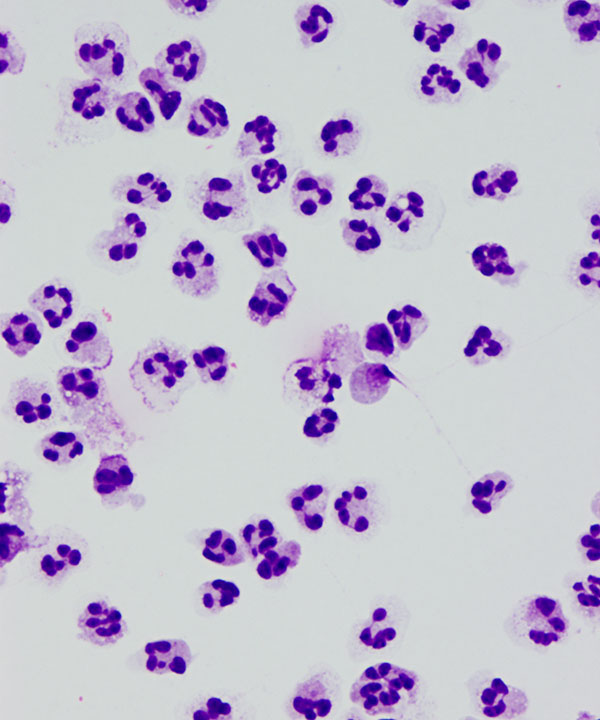
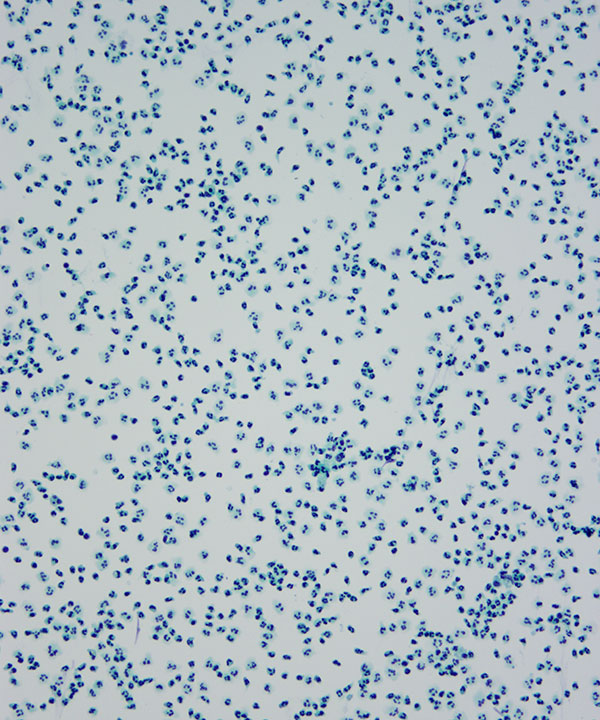
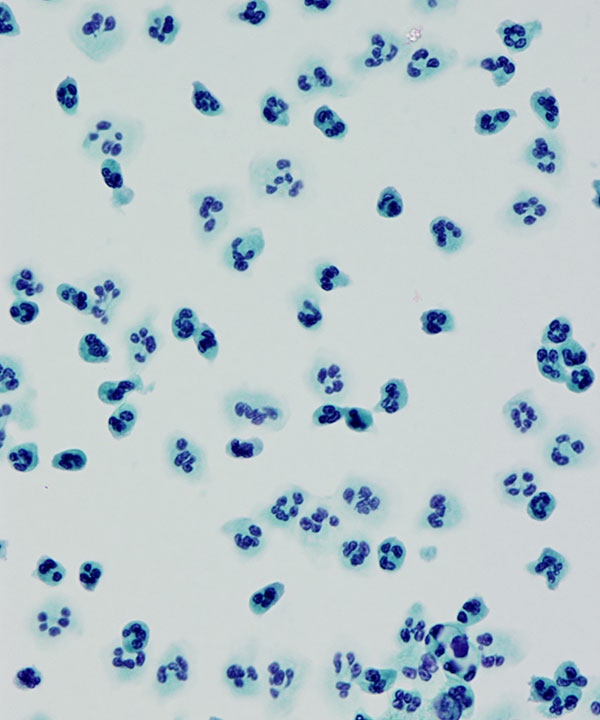
Features
Notes
• Acute inflammation typically indicates bacterial meningitis
• Defined by increased number of neutrophils
• In reparative phase neutrophils disappear
• Most common causes:
- newborns: E.coli, Listeria
- children: Hemophilus, Neisseria, Streptococcus
- adults:Pneumococcus, streptococcus, staphylococcus
Cellular features
• Increased numbers of neutrophils
Background
• May have macrophages
• May have degenerating cells
• May identify microorganisms (culture for definitive diagnosis)