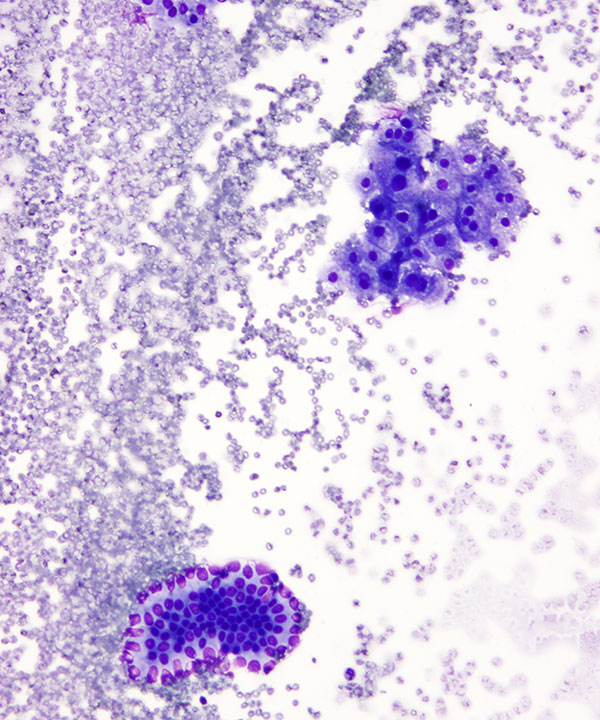
Medium power: DQ stain
Small cluster of hepatocytes (upper right) and bile ductal epithelial cells (bottom left)
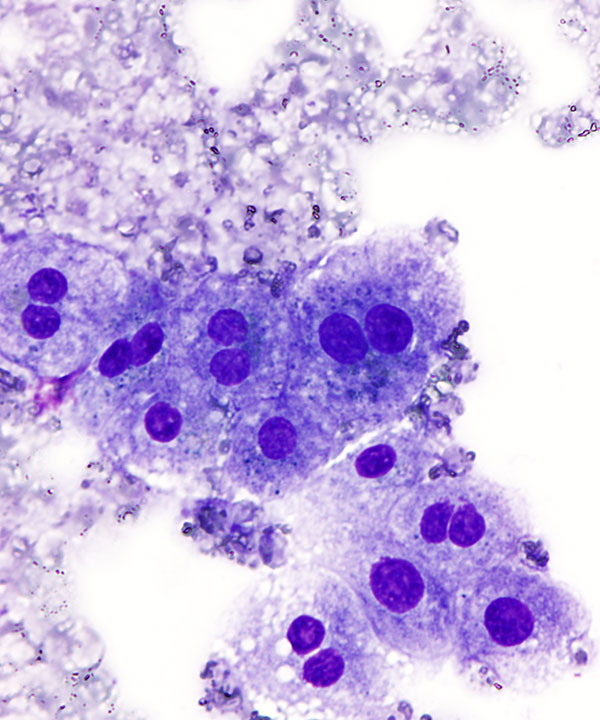
High power: DQ stain
Hepatocytes, large cells with round centrally located nuclei, low N:C ratio, frequent binucleation, and abundant granular cytoplasm containing lipofuscin pigment (blue to purple in DQ stain)
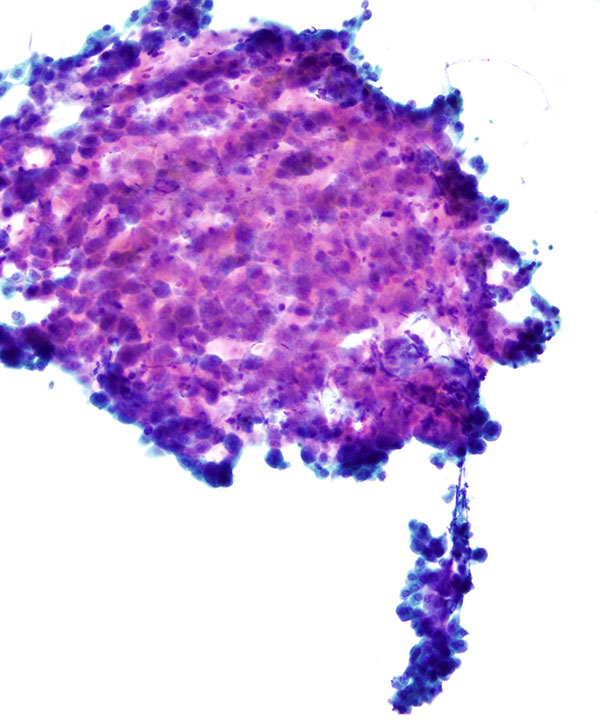
Low power: Pap stain
Small aggregate of hepatocytes arranged in trabeculae, usually 2-3 cells thick
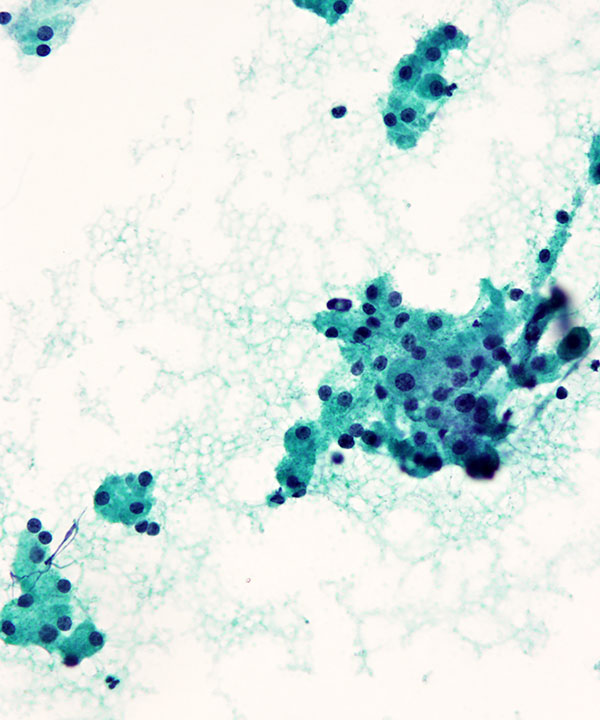
Medium power: Pap stain
Hepatocytes with round centrally located nuclei, low N:C ratio, and abundant granular cytoplasm
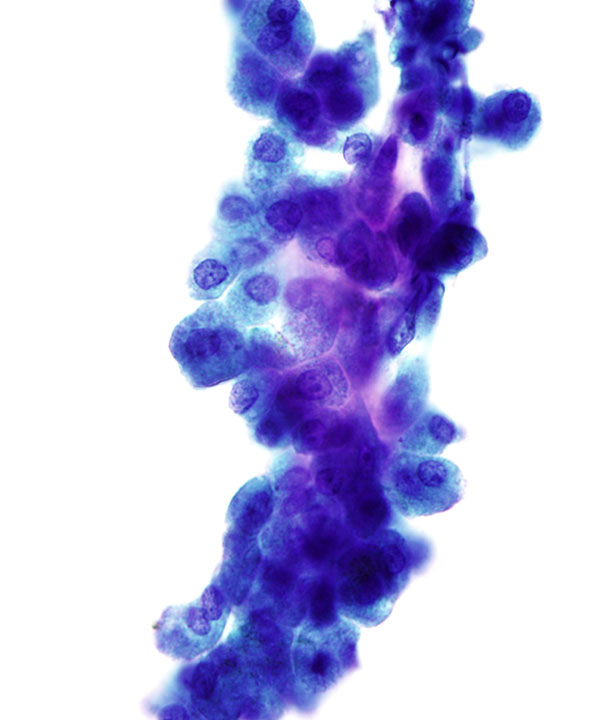
High power: Pap stain
Hepatocytes with round centrally located nuclei, low N:C ratio, frequent binucleation, and abundant granular cytoplasm
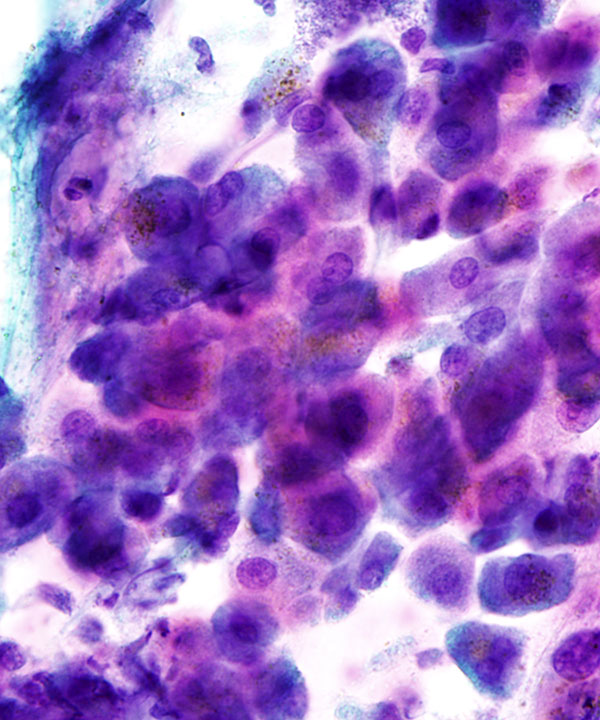
High power: Pap stain
Hepatocytes with intracytoplasmic lipofuscin pigment (orange on Pap stain)
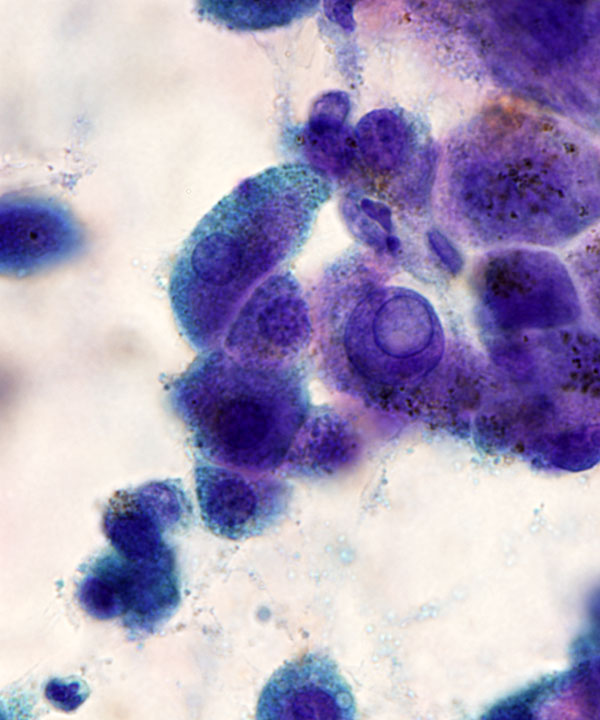
High power: Pap stain
Hepatocytes with intracytoplasmic lipofuscin pigment and intranuclear cytoplasmic inclusion
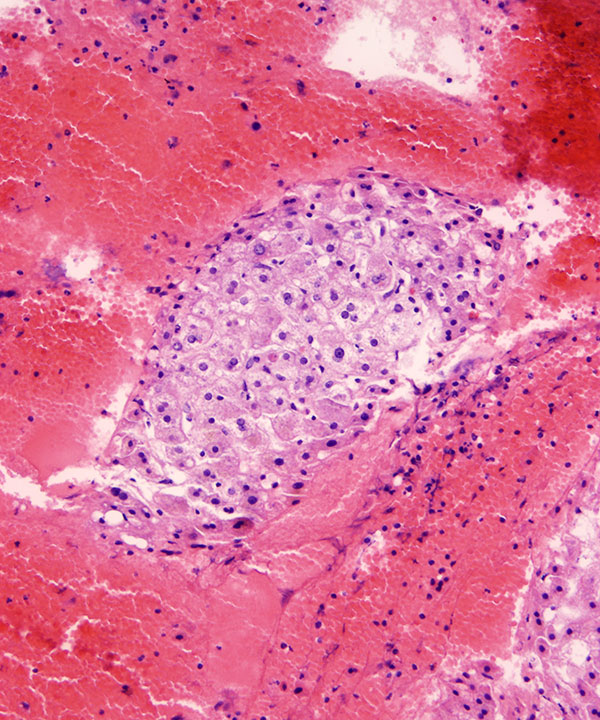
Cell block: H&E stain
Hepatocytes seen within the cell block with low N:C ratios, variation in nuclear size, frequent binucleation and abundant granular cytoplasm
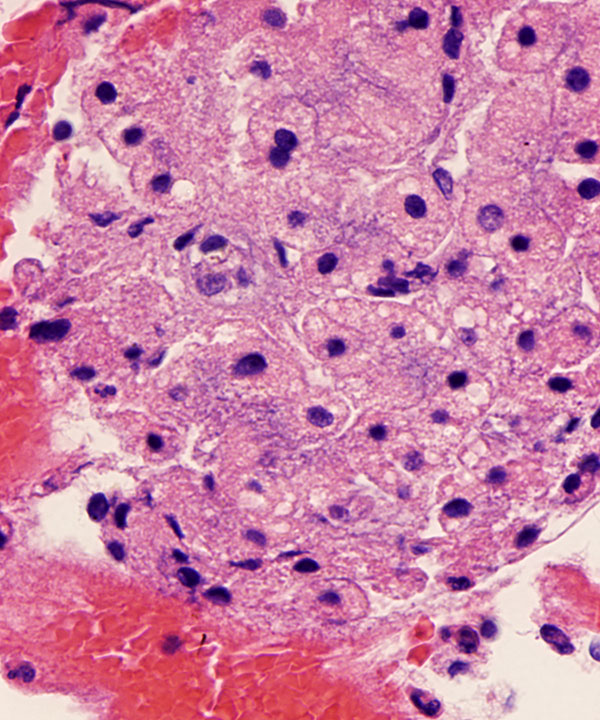
Cell block: H&E stain
Hepatocytes seen within the cell block with low N:C ratios and abundant granular cytoplasm containing lipofuscin
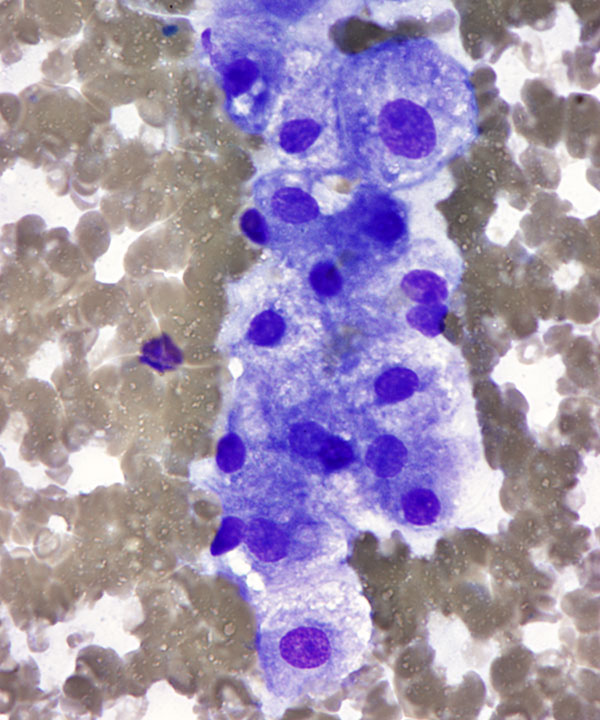
High power: DQ stain
Hepatocytes with fatty change (steatosis)
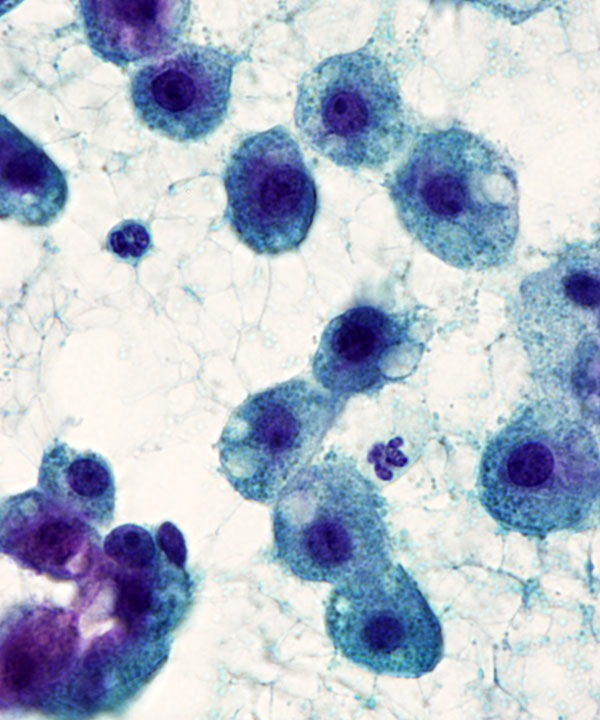
High power: Pap stain
Hepatocytes with fatty change (steatosis)
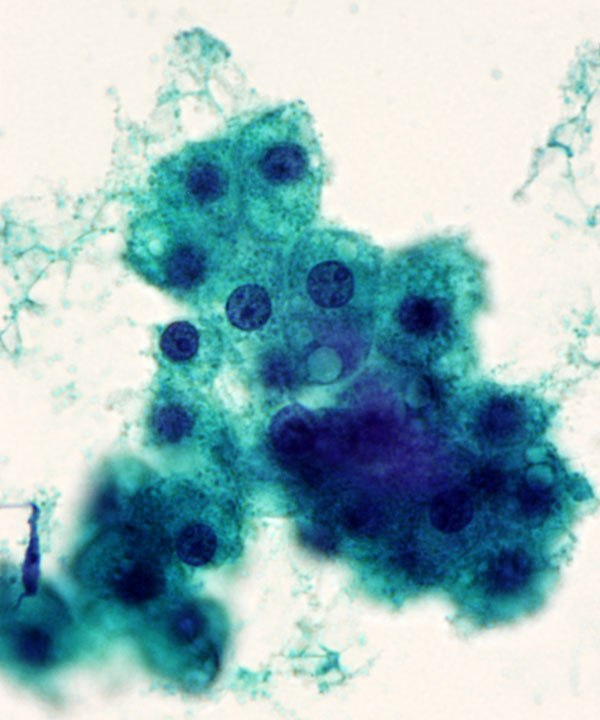
High power: Pap stain
Hepatocytes with fatty change (steatosis)
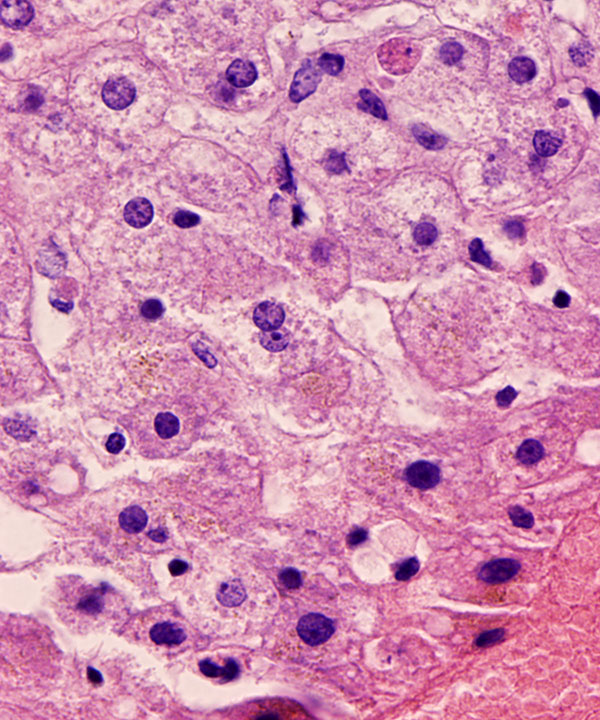
Cell block: H&E stain
Steatosis seen in the corresponding cell block sections
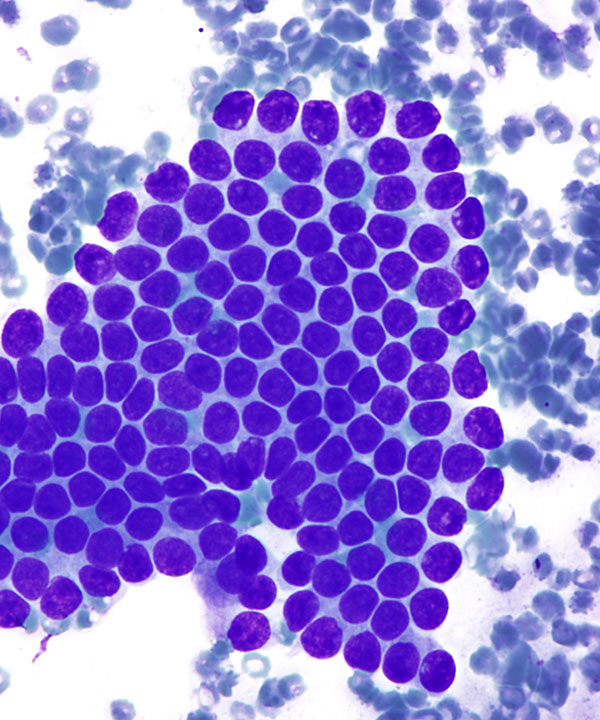
High power: DQ stain
Bile ductal epithelial cells forming 2-dimensional flat sheet with orderly uniform round nuclei and smooth nuclear membranes
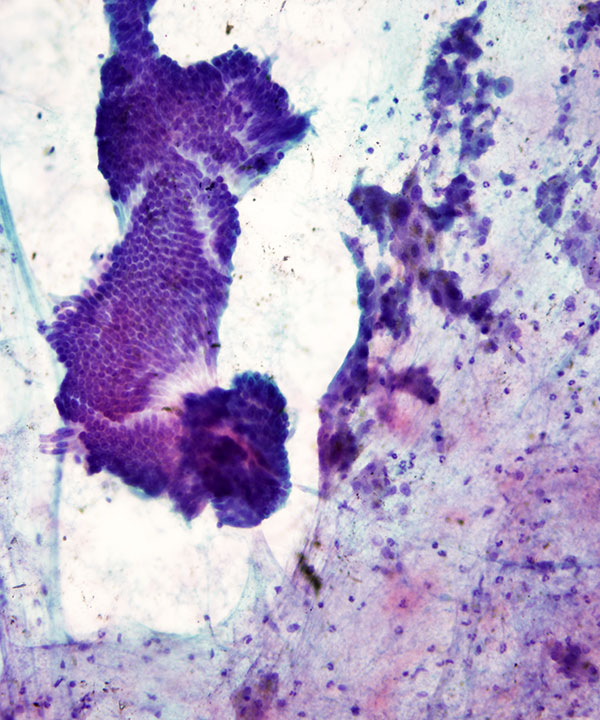
Low power: Pap stain
Bile ductal epithelial cells forming cohesive sheet of small orderly uniform cells. Also seen are benign hepatocytes (right)
Features
• Hepatocytes and bile ductal epithelial cells
• Other cells that may be seen:
– Kupffer cells (resemble macrophages)
– Endothelial cells (spindle cells outlining trabeculae)
• Hepatocytes are typically in trabecular arrangements (usually 2 - 3 cell thick)
• Bile duct cells are in 2D flat cohesive sheets
• Hepatocytes
– Large round to polygonal cells
– Low N:C ratio
– Abundant granular cytoplasm
– May have intracytoplasmic pigment or lipid
• Hepatocytes
– Nuclei are round centrally located
– Variation in nuclear size common
– Binucleation/ multinucleation common
– Intranuclear cytoplasmic inclusions may be seen
– Nucleoli visible to prominent
• Hepatocyte cytoplasmic inclusions
– Hyaline globules (dense round eosinophilic globules, PAS+)
– Mallory bodies (ropy fibrillar, hyaline inclusions surrounding nucleus)
– Councilman bodies (apoptotic mummified hepatocytes, dense and eosinophilic)
• Hepatocyte cytoplasmic pigments
– Lipofuscin (wear and tear pigment, blue• green on DQ, red orange on Pap)
– Bile (peri-or intracanalicular, blue green in DQ and Pap)
– Hemosiderin (coarse, blue• green on DQ and golden brown on Pap and refractile)