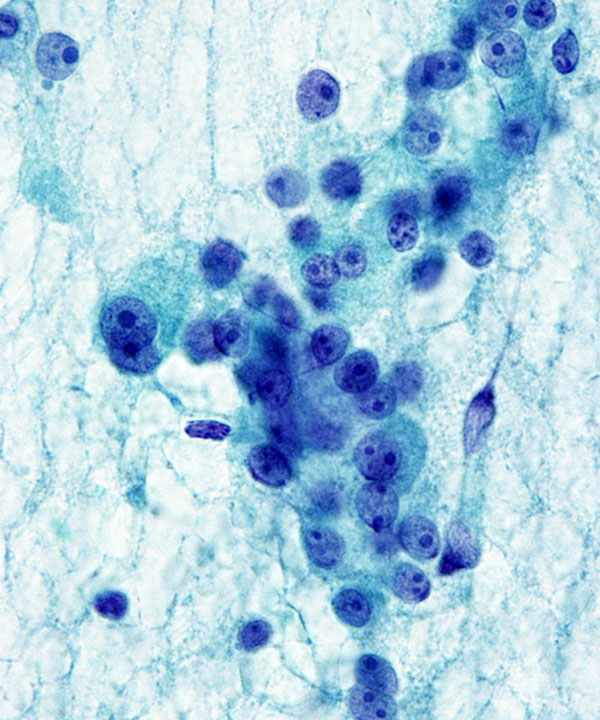
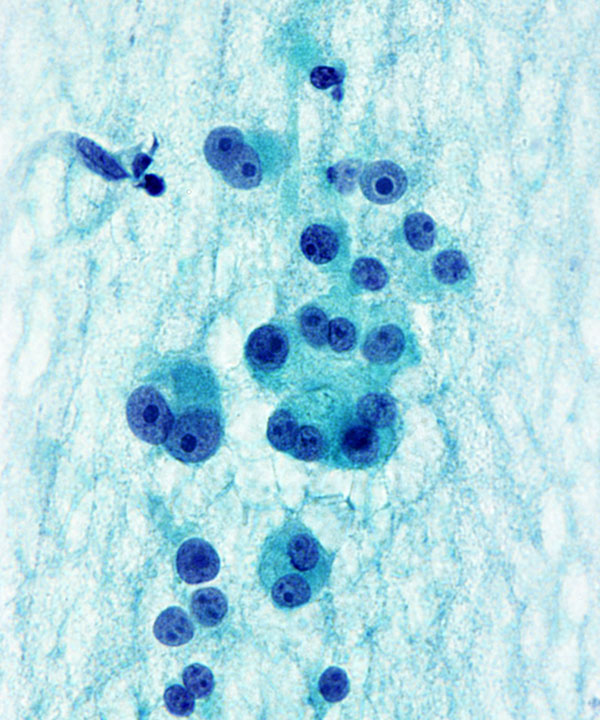
Features
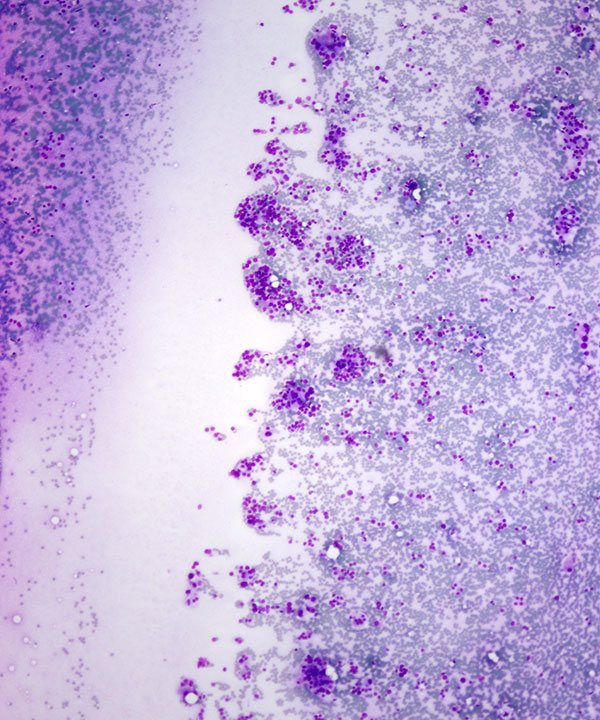
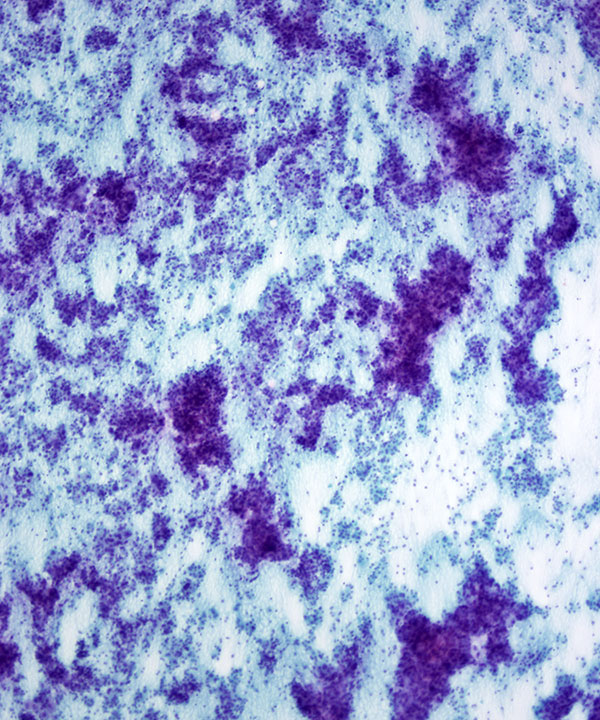
• Cellular smears, predominantly Hürthle cells
• Crowded, 3D clusters
• Flat sheets favor benign
• May have papillary architecture
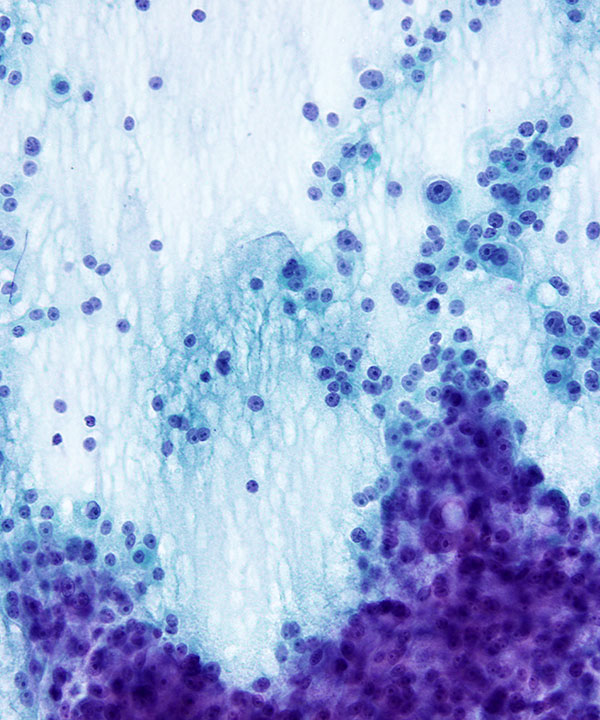
• May have single cells
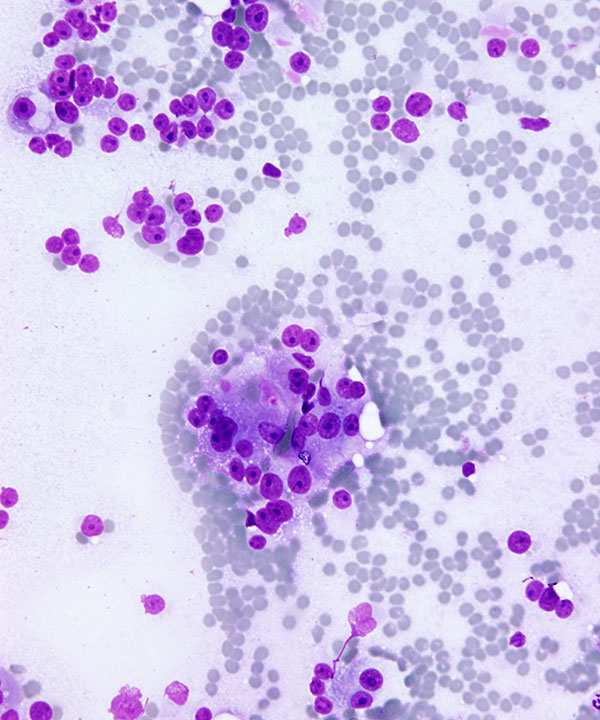
• Oncocytic cells
• May be bland
• May have atypia or pleomorphism
• Granular cytoplasm
• Intracytoplasmic vacuoles may be present
• High N:C ratio favors malignant
• Nuclei are round/oval,eccentrically located
• Fine to coarse chromatin
• Bi/multinucleation may be present
• Prominent nucleoli present
• Intranuclear cytoplasmic inclusions may be seen
• Scant to absent colloid
• May have cystic change (histiocytes, hemorrhage, giant cells)
• May have naked nuclei (favor malignant)
• Transgressing vessels may be seen
• Similar to follicular neoplasms, cytologic atypia, mitoses and necrosis are not indicators of malignancy. Histologic evidence of invasion or metastasis is required for a diagnosis of Hurthle cell carcinoma.
• Sensitivity of FNA diagnosis of Hürthle cell carcinoma is high but specificity is low, so recommended diagnosis is Follicular neoplasm, Hürthle cell type.
• Express thyroglobulin, may express Galectin-3, S100
Montone KT et al. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2008 Aug;132(8):1241-50.
Pambuccian SE et al. Acta Cytol. 1997 Jan-Feb;41(1):197-208.
Gonzalez JL et al. Am J Clin Pathol. 1993 Sep;100(3):231-5.
Kini SR et al. Acta Cytol. 1981 Nov-Dec;25(6):647-52.