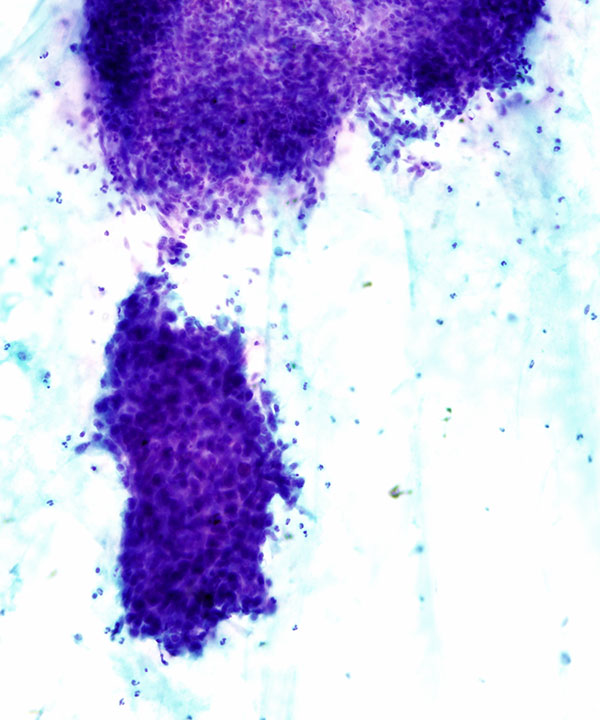
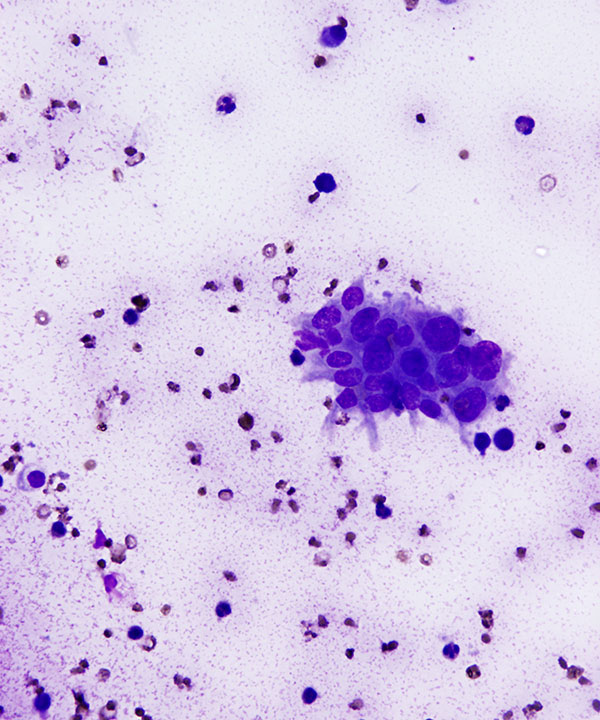
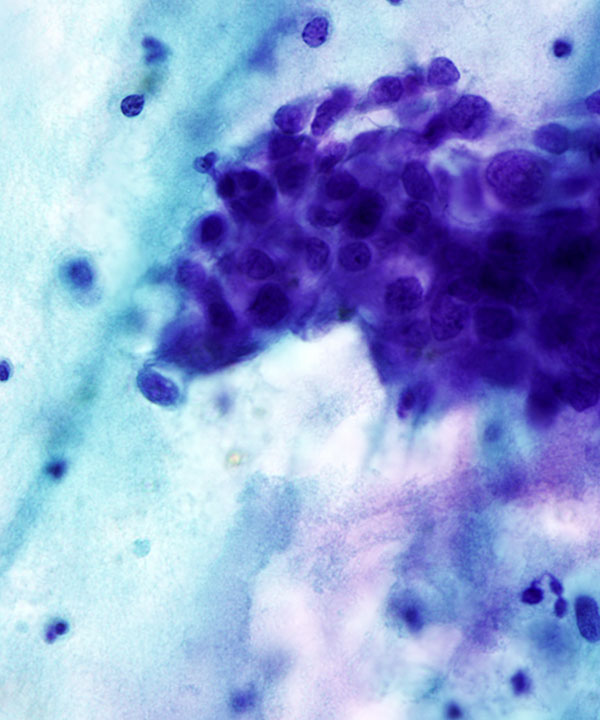
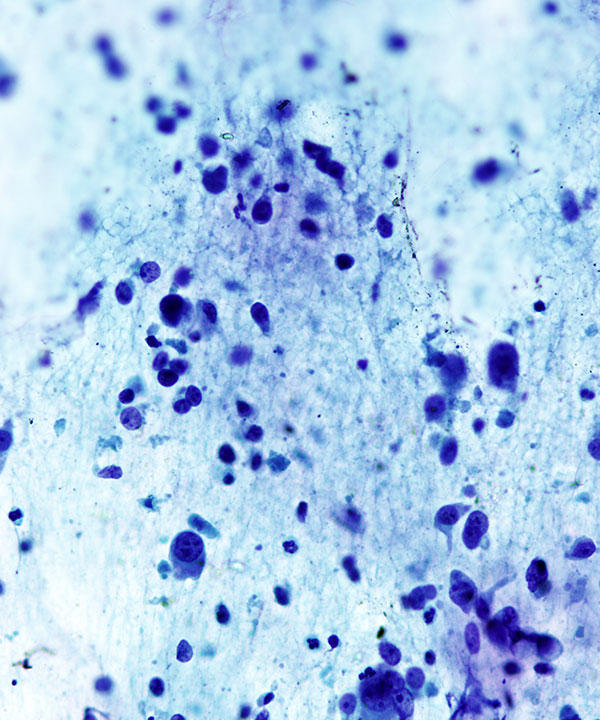
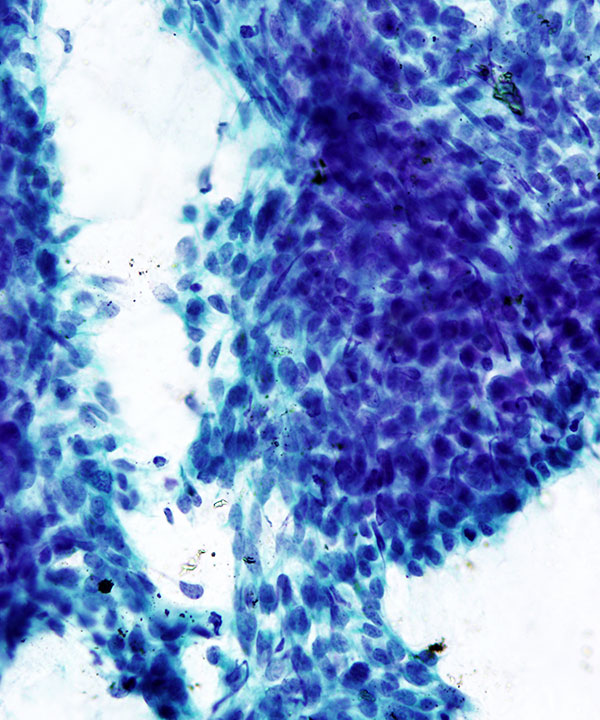
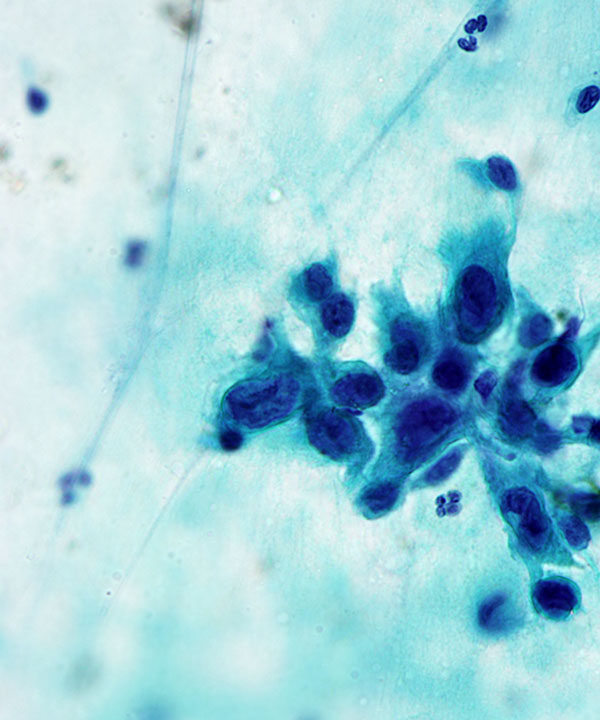
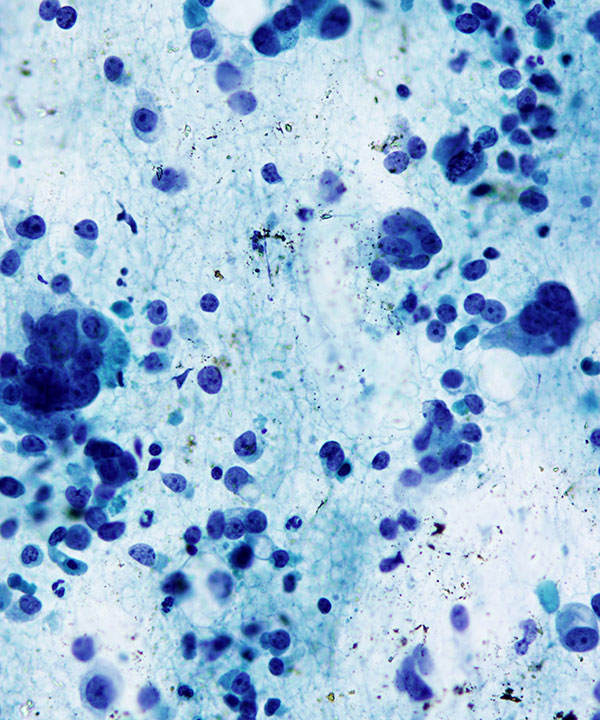
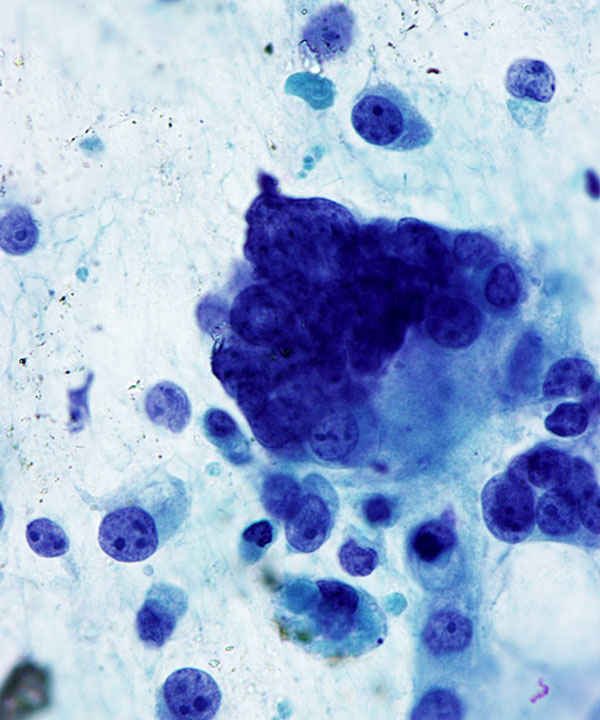
Features
• Cellular with highly malignant features
• Single cells and loosely cohesive clusters
• Epithelioid, spindled and giant cells
• Epithelioid cells may be plasmacytoid
• Pale to granular cytoplasm
• May have dense squamoid cytoplasm
• Nuclei enlarged, irregular contours
• Coarse chromatin
• Prominent nucleoli, macronucleoli
• Multinucleation
• Often has intranuclear cytoplasmic inclusions
• Dirty, necrotic background
• May have abundant neutrophils
• May have myxoid/ cartilageneous/ osseous metaplasia
• Typically rapidly enlarging highly malignant tumor
• May arise de novo or transformation of other thyroid carcinoma, typically papillary thyroid carcinoma
• May detect a more differentiated cytomorphology
• Cytokeratin +/- , vimentin may be positive ; typically negative for TTF-1, thyroglobulin, EMA, CEA
Us-Krasovec M et al.Acta Cytol. 1996 Sep-Oct;40(5):953-8.
Guarda LA et al. Diagn Cytopathol. 1991;7(1):63-7.