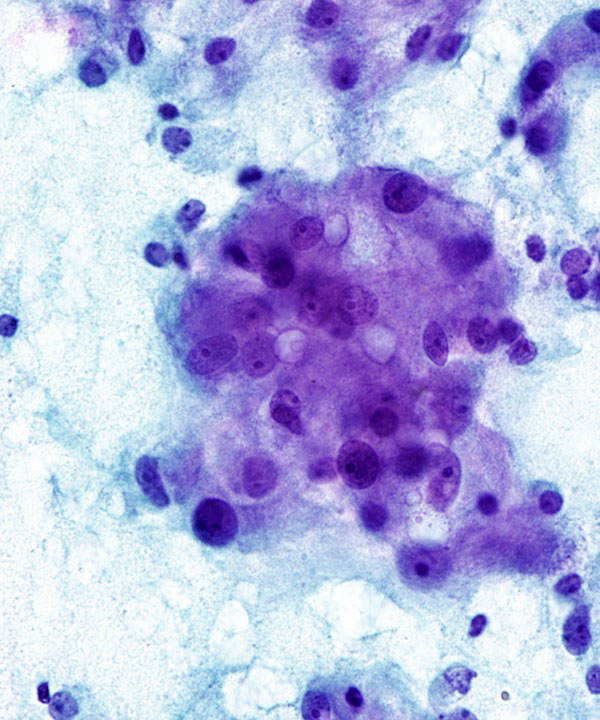
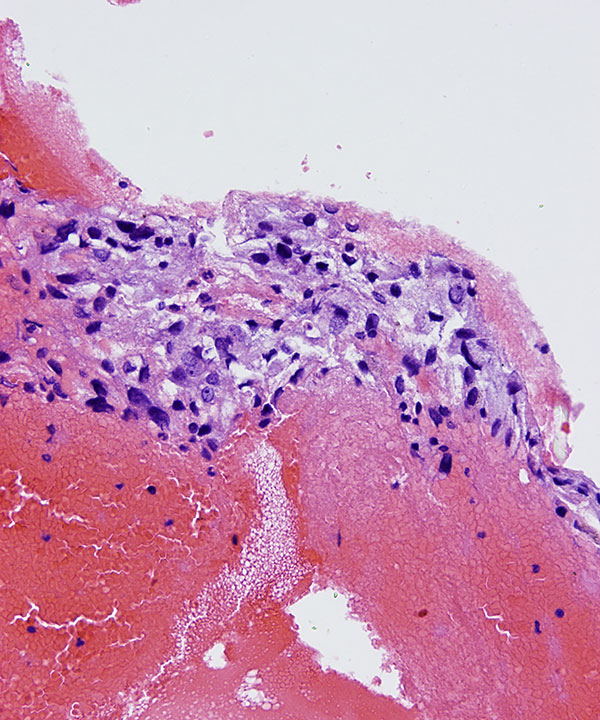
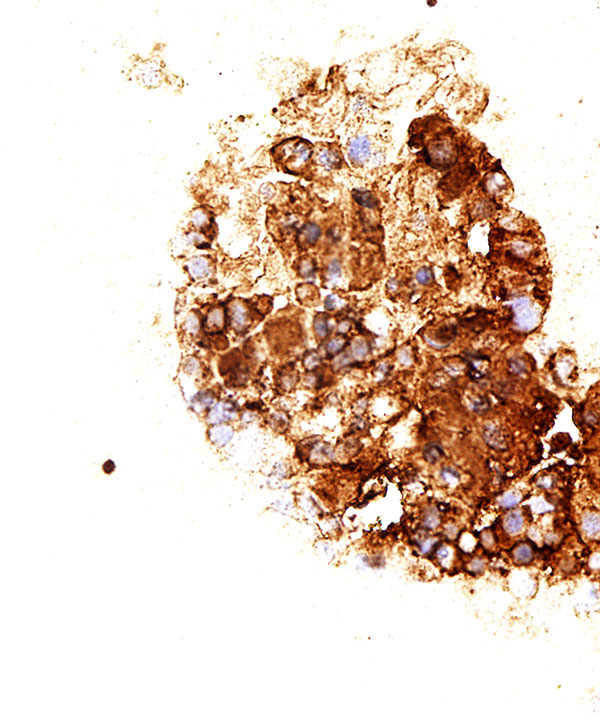
Features
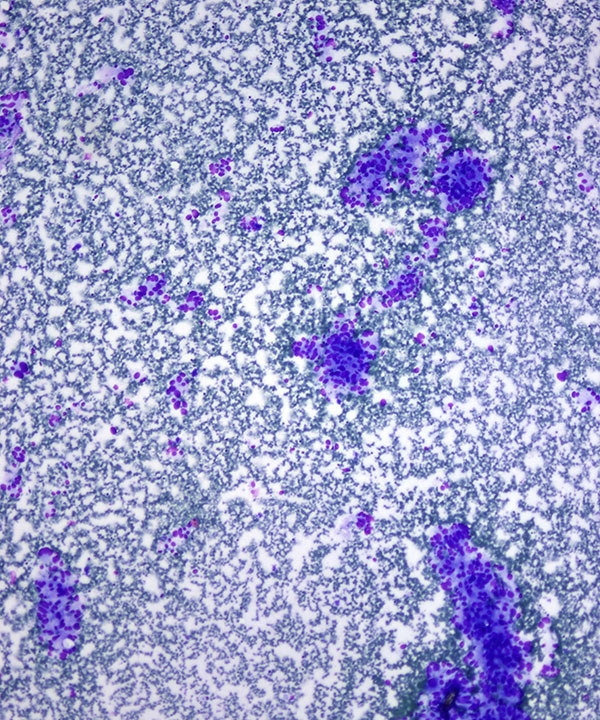
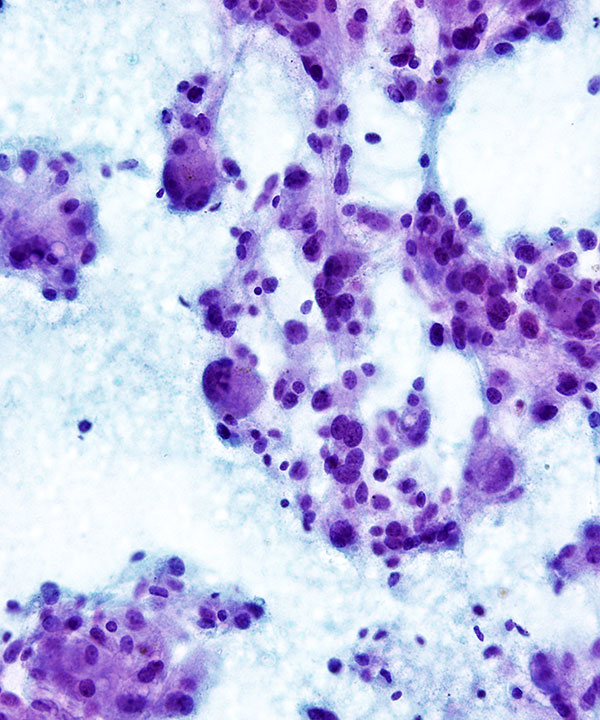
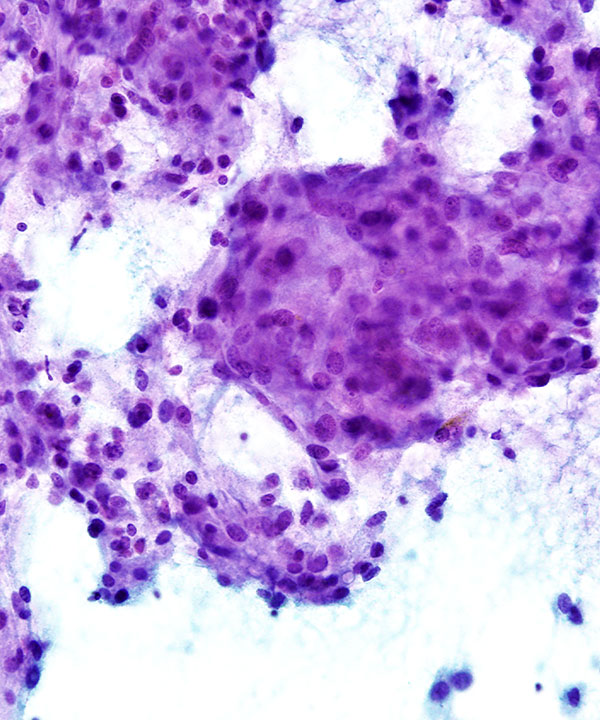
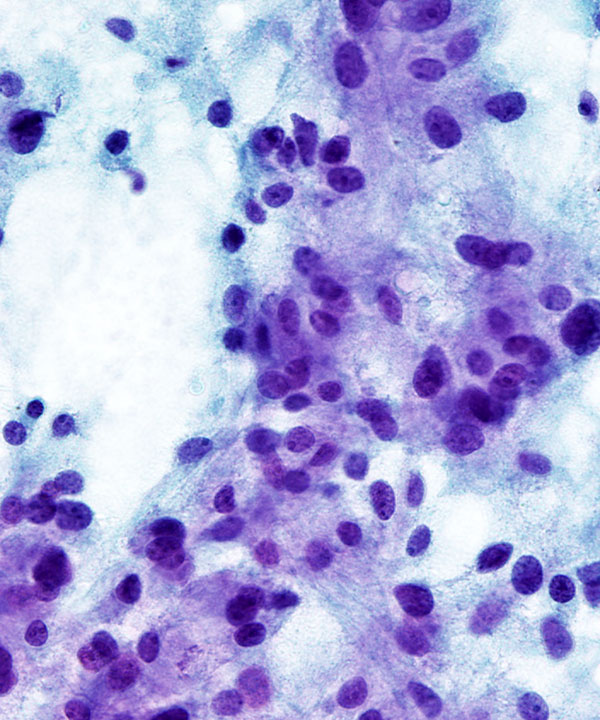
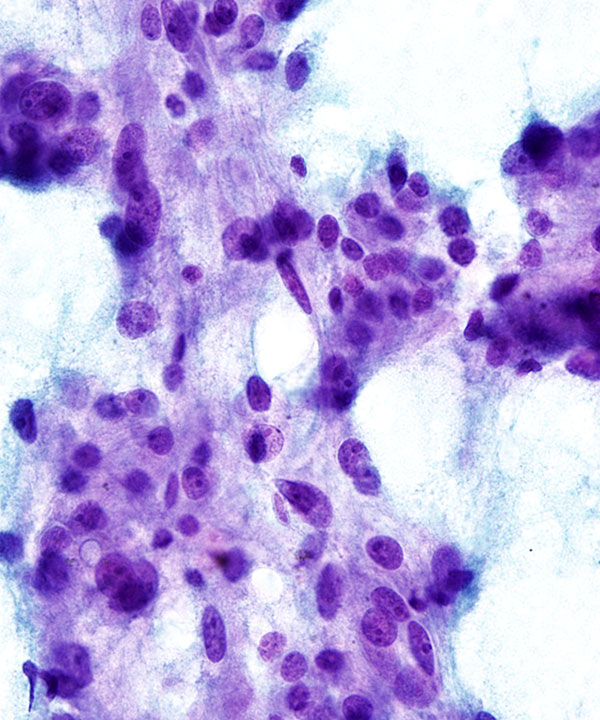
• Cellular smears
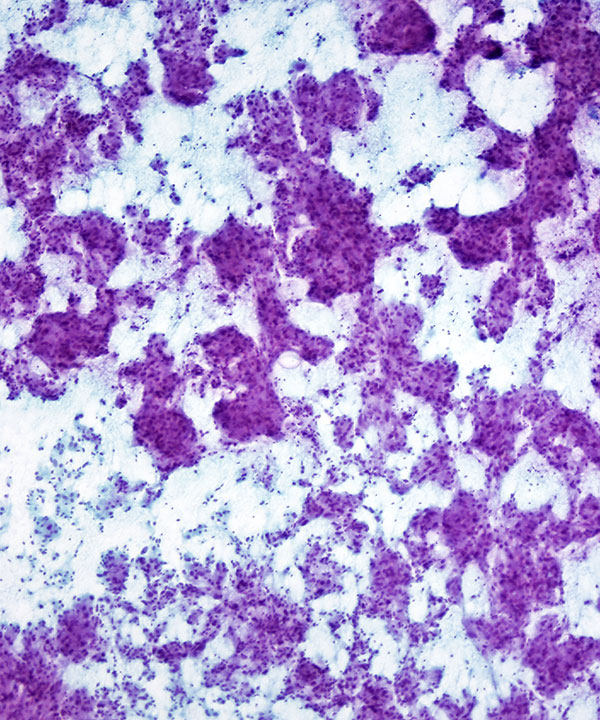
• Loosely cohesive groups, single cells and rosettes
• May have zellballen (cell ball) appearance
• Anaplasia usually does not correlate with malignancy
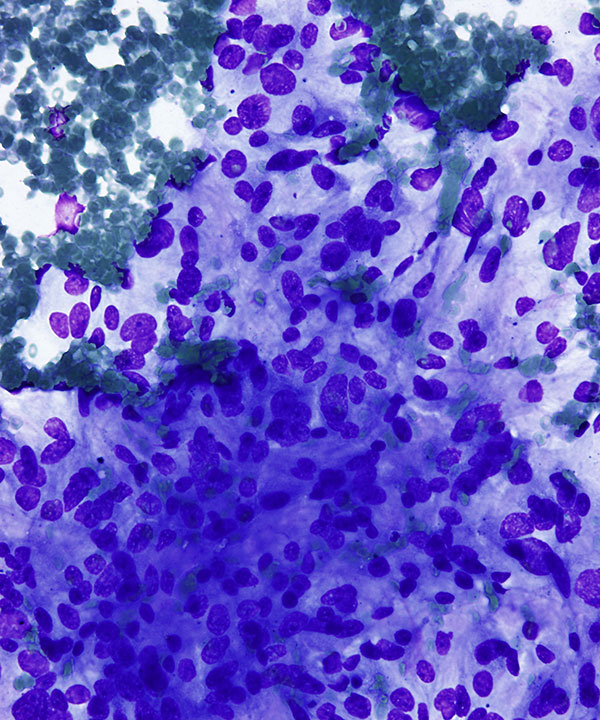
• Epithelioid and spindle cells
• Cytoplasm granular with red neurosecretory granules
• May have intracytoplasmic lipid droplets
• May have intracytoplasmic hyaline globules
• Melanin pigment rarely seen
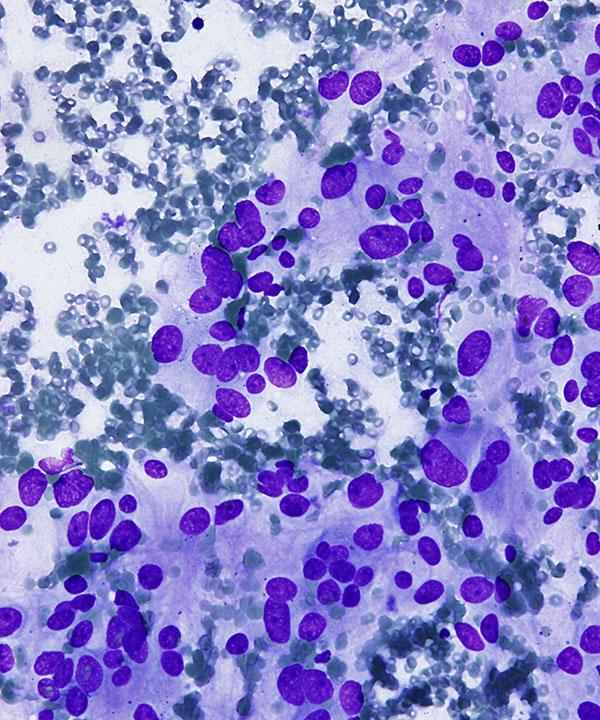
• Nuclei round to oval to pleomorphic
• Binucleation and multinucleation
• May have stippled chromatin (salt and pepper)
• May have prominent nucleoli
• Nuclear atypia is not an indicator of malignancy
• May have mitosis
• May have ganglion cells
• May have spindle/stellate sustentacular cells
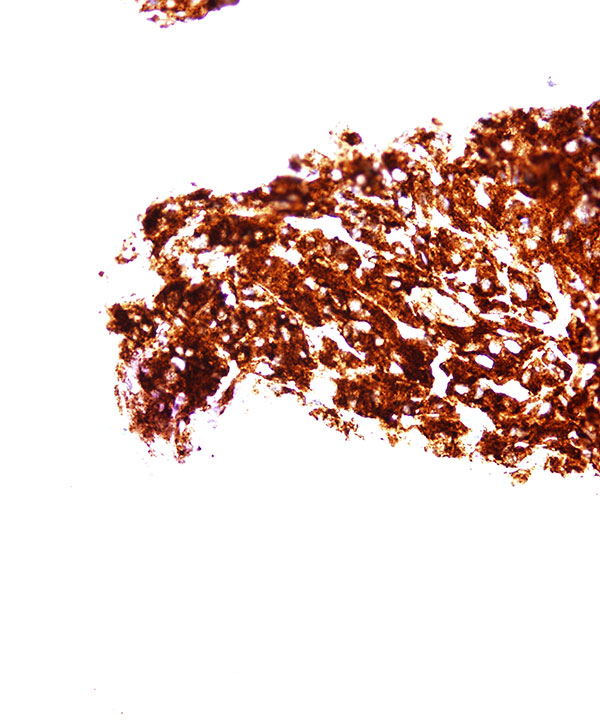
• Positive for synaptophysin, chromogranin and CD56.
• Sustentacular cells are usually S100 positive.
• Negative for Inhibin and Melan A, usually negative for cytokeratin.
• RET, VHL, NF1, SDH
• Adrenal cortical adenoma/hyperplasia
• Adrenal cortical carcinoma: inhibin and synaptophysin positive (cytoplasmic), chromogranin negative (cytoplasmic)
• Renal cell carcinoma: pax-8 positive (nuclear), Melan A and inhibin negative (cytoplasmic)
• Metastatic Tumors: more likely to be bilateral, use clinical/radiographic history and site specific immunocytochemical markers if needed
Jimenez-Heffernan JA et al. Acta Cytol. 2006 Jul-Aug;50(4):372-8.
Wagnerova H et al. Bratisl Lek Listy. 2013;114(4):237-40.