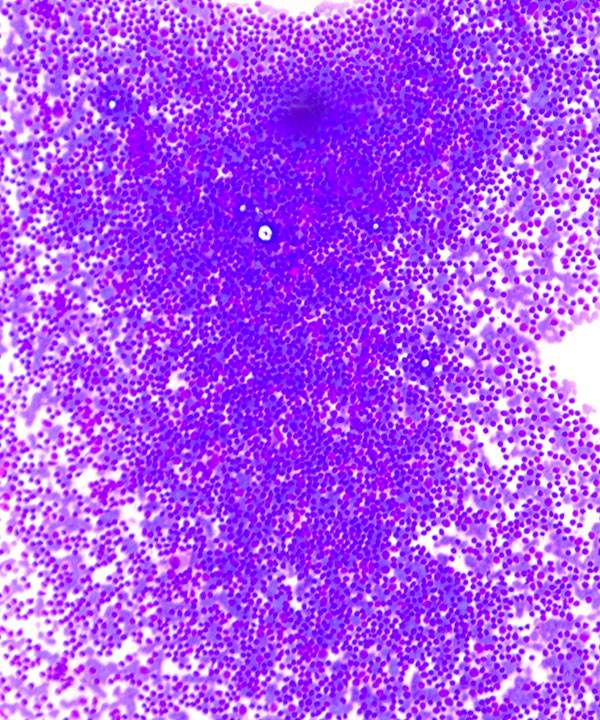
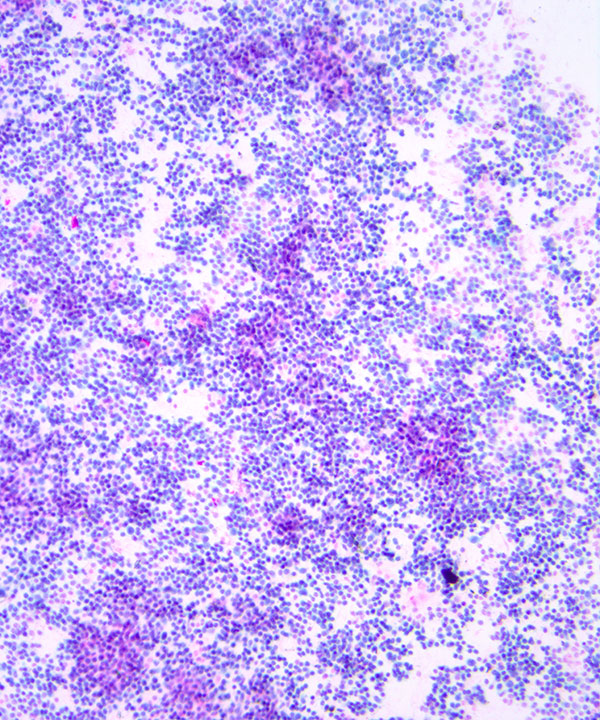
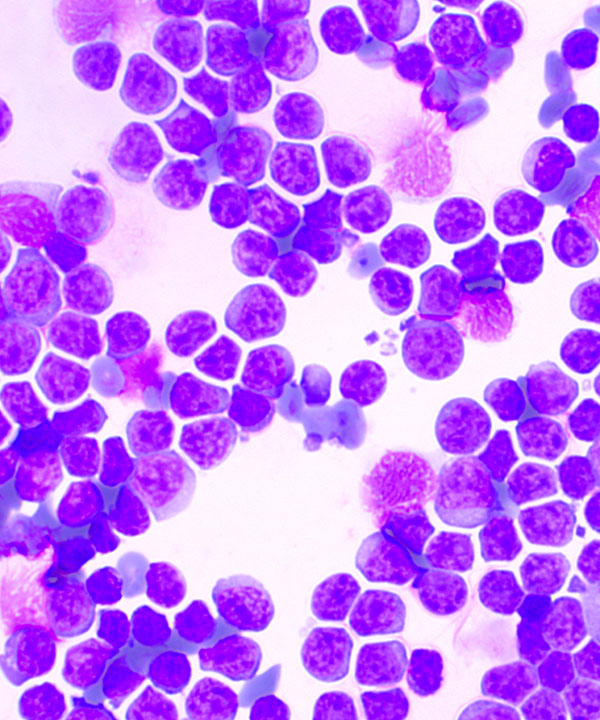
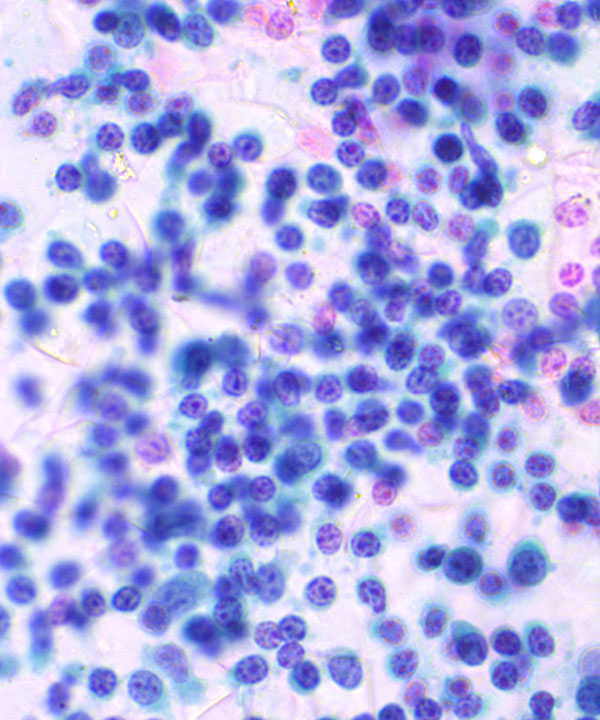
Features
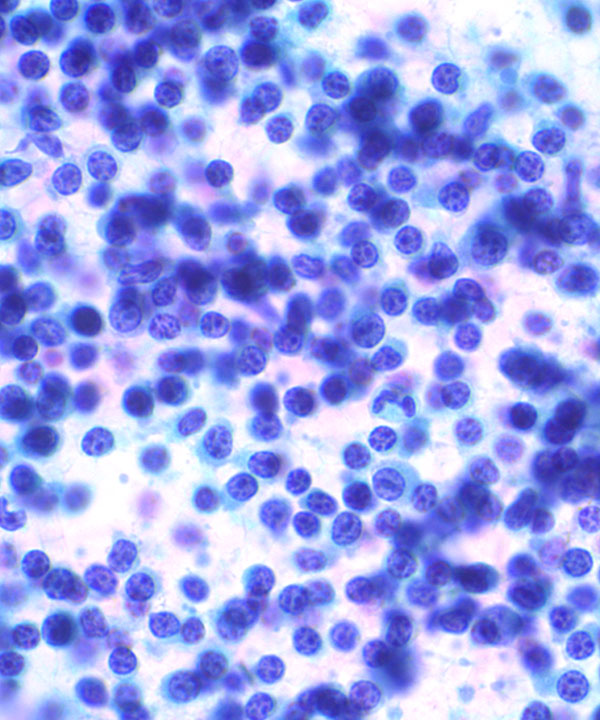
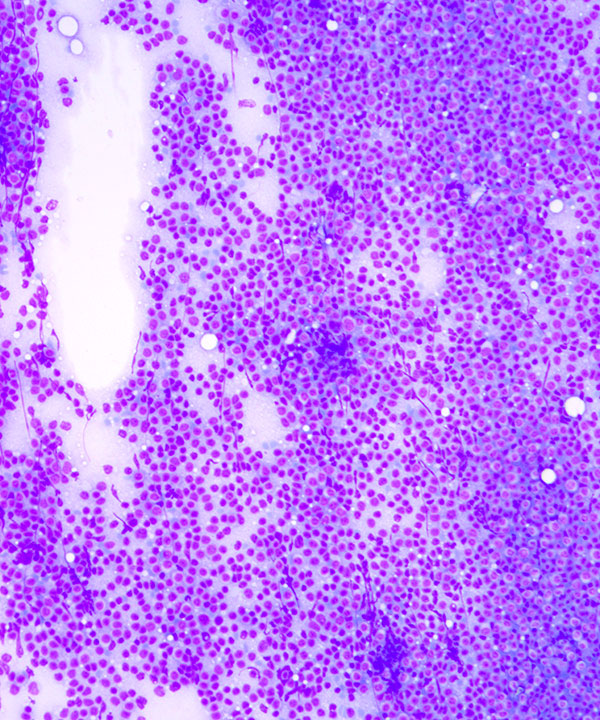
• Dispersed lymphoid cells
• Monomorphic population
• Predominately small monomorphic lymphoid cells (same size or slightly larger than normal lymphocytes)
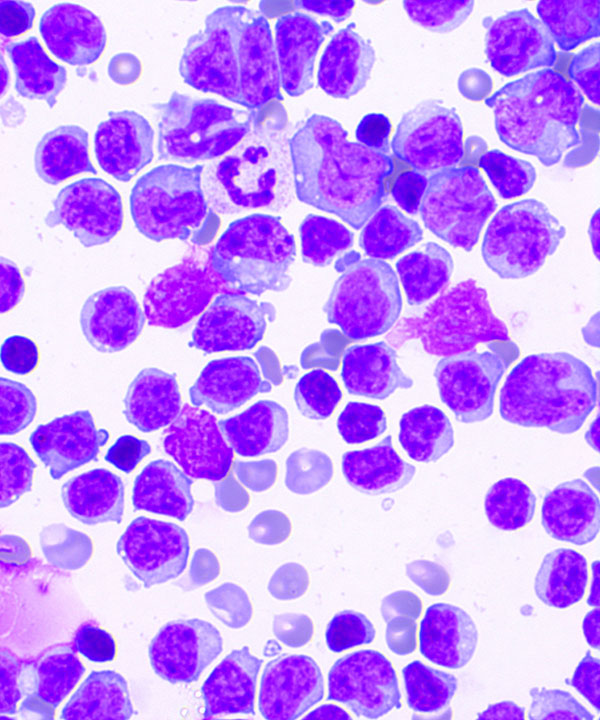
• Scattered rare prolymphocytes and paraimmunoblasts (medium to large in size)
• Scant cytoplasm in small lymphoid cells
• Cytoplasm more abundant in paraimmunoblasts
• Small lymphoid cells:
- round nuclei
- clumped soccer ball or cracked mud chromatin
• Prolymphocytes:
- dispersed chromatin
- distinct nucleoli
• Paraimmunoblasts:
- round to oval nuclei
- dispersed chromatin
- central nucleoli
• Typically positive for CD20 (can be weak), CD5, CD23
• Negative for CD10, Cyclin D1
• Typically express CD45 (bright), CD19, CD20(dim), CD5, CD23, CD43, CD200; kappa or lambda light-chain restriction (can be dim)
• Negative for CD10, FMC7
Favorable prognosis
• Isolated deletion 13q14
• Somatic hypermutation in IgVH (>2% variance from germline sequence)
Unfavorable prognosis
• Trisomy 12
• Deletion 11q22-23 (ATM) - high WBC and lymphadenopathy
• Deletion 6q21
• Caraway NP, Stewart JM. Small lymphocytic lymphoma. Diagnostic Pathology Cytopathology. First Edition. DR Mody. Manitoba: Amirsys, 2014. III-4-20-III-4-21. Print.
• Muller-Hermelink HK, Montserrat E. et al. Chronic lymphocytic leukaemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma. WHO Classification of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues. Fourth Edition. Steven H. Swerdlow. Lyon: 2008. 180-182. Print.