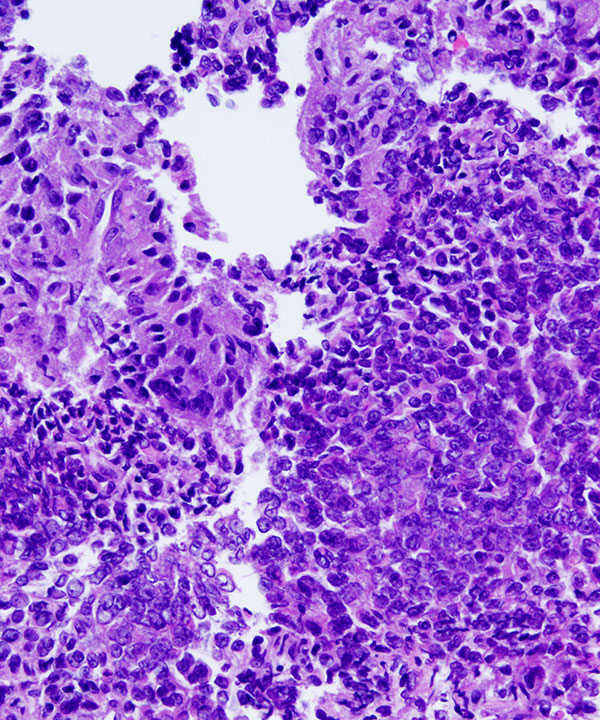
Features
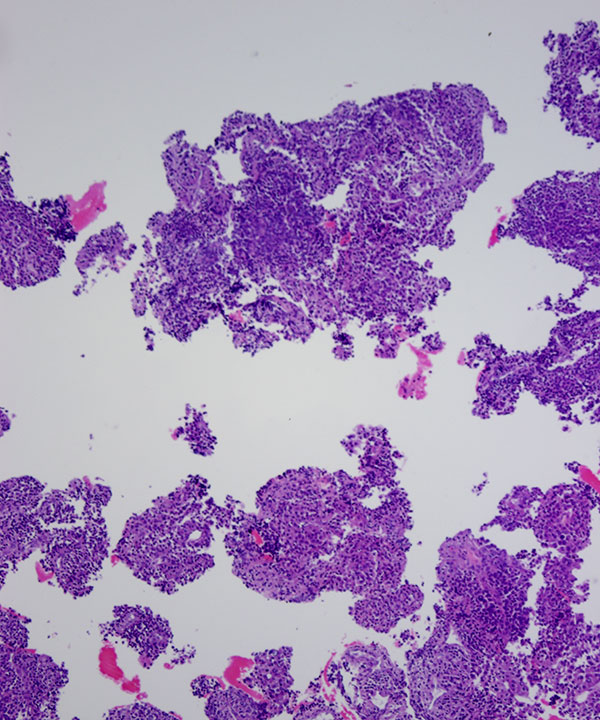
• Diffuse growth pattern
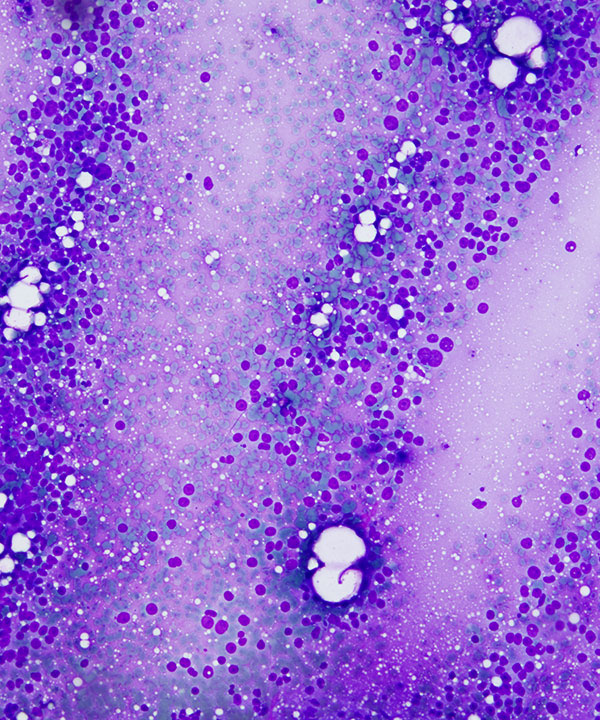
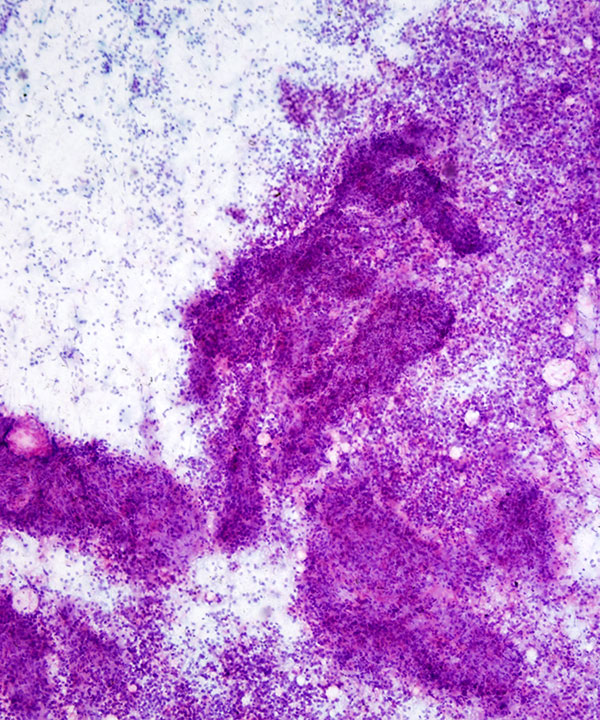
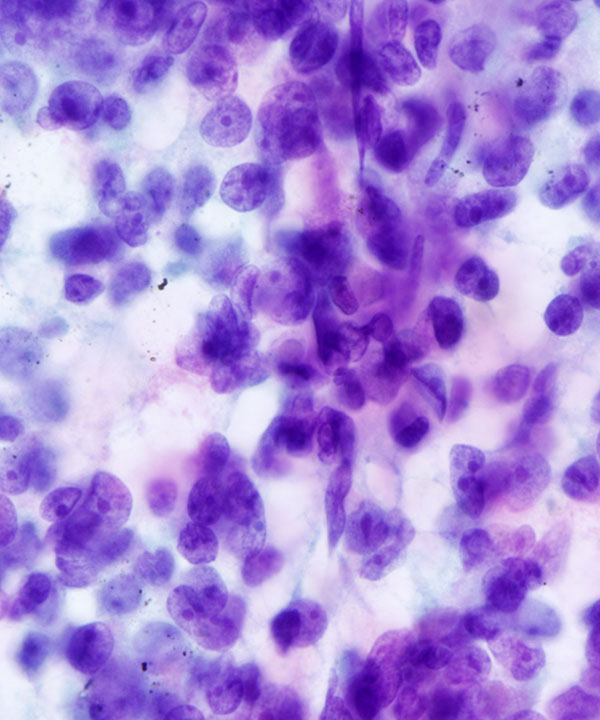
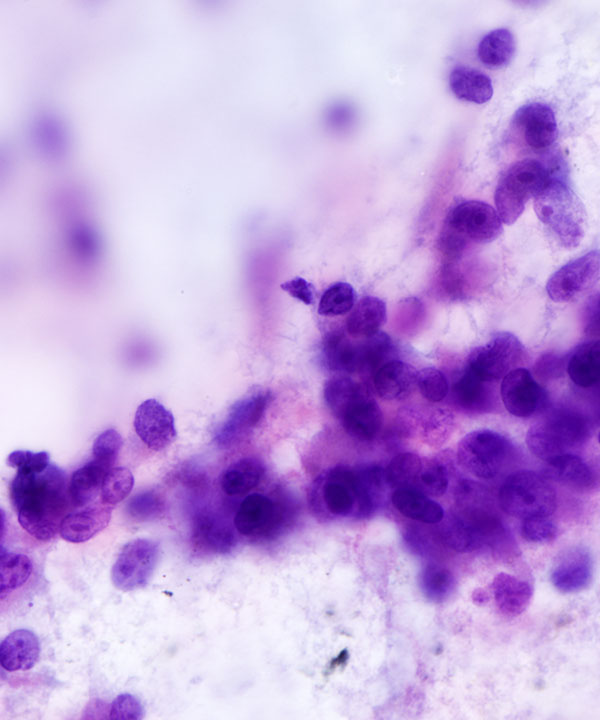
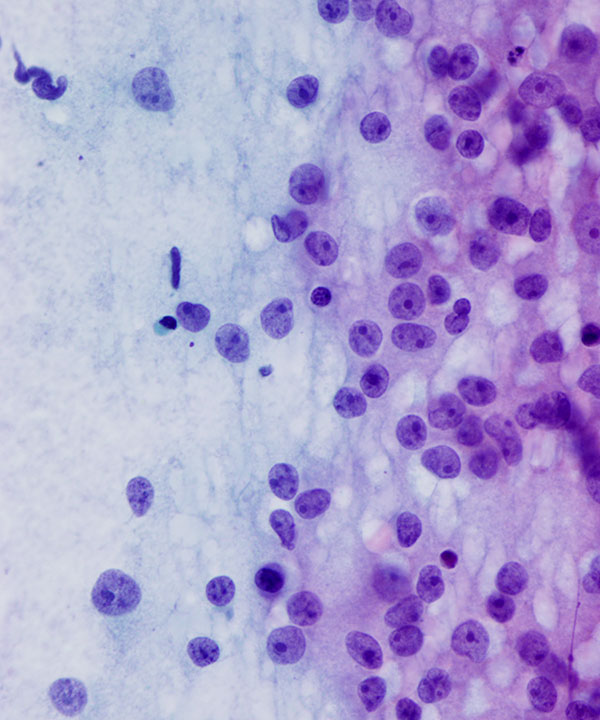
• Cellular smear with cohesive clusters and single intact cells
• Capillaries traversing and wrapping cell clusters
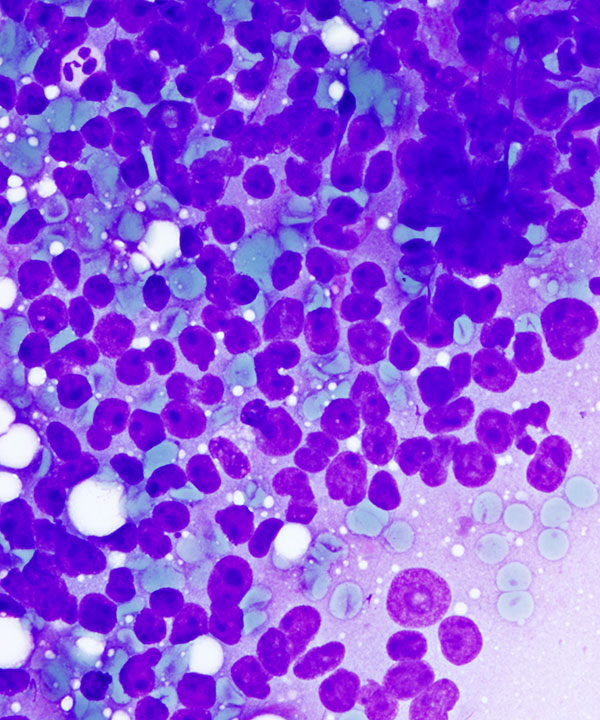
• Bland low N:C ratio cells to anaplastic malignant looking cells
• Epithelioid or spindled
• May have multinucleated bizarre cells
• Cytoplasm vacuolated but usually preserved
• May have granular cytoplasm
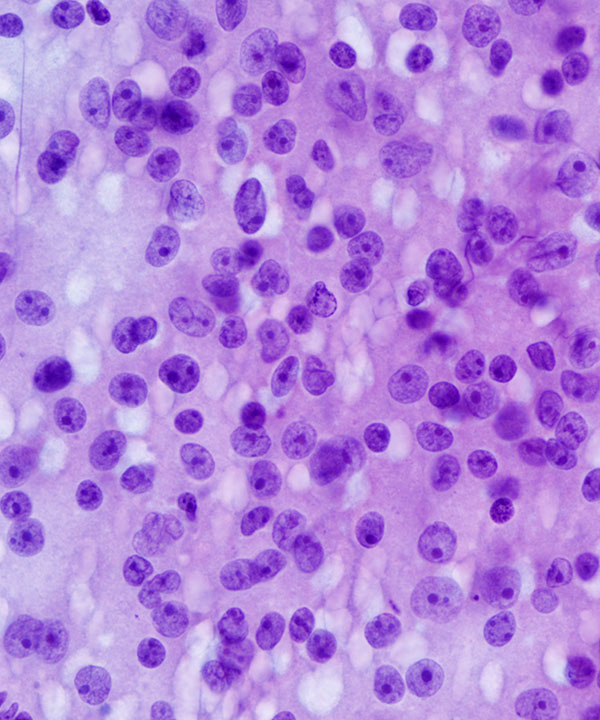
• Nuclei may be enlarged, hyperchromatic, irregular, pleomorphic
• Coarse chromatin
• Prominent nucleoli
• May have intranuclear cytoplasmic inclusions
• Naked nuclei less common
• Mitosis common, including atypical mitoses
• Usually necrosis present
• Foamy background less common
• Positive stains: inhibin (cytoplasmic), Melan A (cytoplasmic), calretinin (cytoplasmic and nuclear), synaptophysin +/- (cytoplasmic)
• Negative stains: chromogranin (cytoplasmic), pax-8 (nuclear)
• Adrenal cortical adenoma/hyperplasia
• Pheochromocytoma: chromogranin positive (cytoplasmic), Melan A and inhibin negative (cytoplasmic)
• Renal cell carcinoma: pax-8 positive (nuclear), Melan A and inhibin negative (cytoplasmic)
• Metastatic Tumors: more likely to be bilateral, use clinical/radiographic history and site specific immunocytochemical markers if needed
Saboorian MH et al. Acta Cytol. 1995 Sep-Oct;39(5):843-51.
Tirabassi et. al. J Endocrinol Invest. 2012 Jun;35(6):590-4.
Wagnerova H et al. Bratisl Lek Listy. 2013;114(4):237-40.