Features
Notes
• Primary CNS lymphomas rare
• Most common in children: lymphoblastic and Burkitt
• Most common in adults: large B-cell, high grade follicular, Burkitt
• Low-grade lymphomas, Hodgkin, myeloma, T-cell lymphomas relatively rare
• Difficulty in diagnosing if few cells present
• Repeat sampling/flow cytometry/ immunocytochemistry may be needed
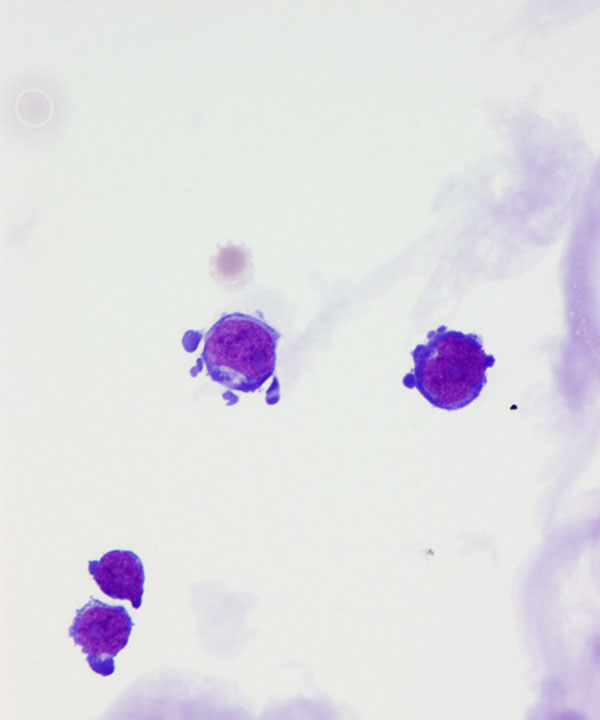
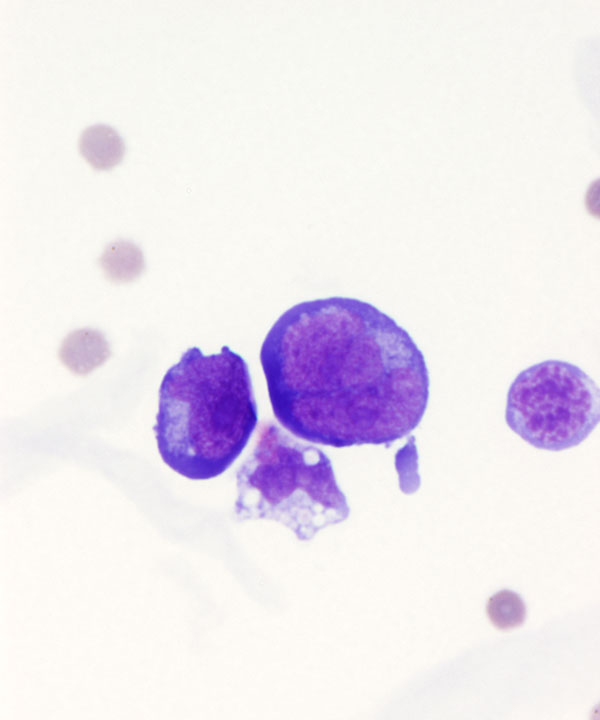
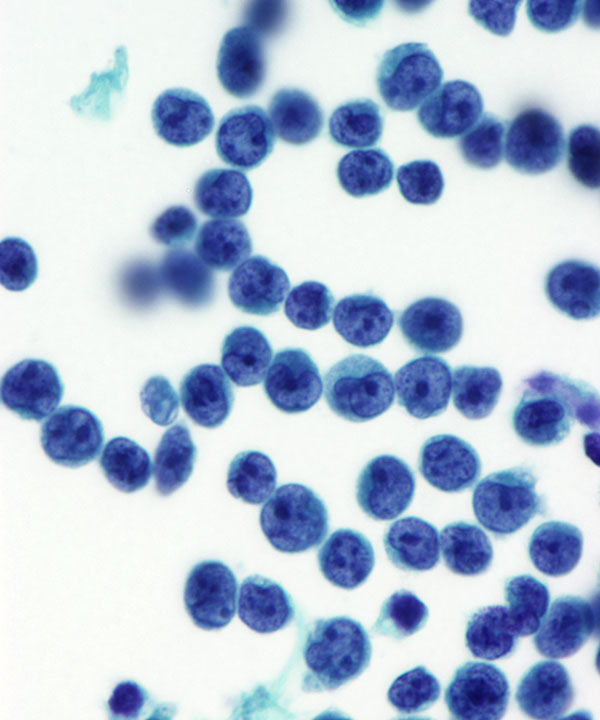
Cellular features
• Cellularity varies
• Malignant cells usually larger than normal lymphocytes
• Cytoplasm usually scant, blue (on DQ stain) and may show vacuoles
Nuclear features
• Nuclei enlarged
• Nuclei with irregular/ lobulated/ protruding outlines
• Chromatin usually coarse and hyperchromatic in lymphoma
• Chromatin usually fine and powdery like blasts in lymphoblastic lymphoma
• May have prominent nucleoli