Features
• Most common cause of malignant effusions with adenocarcinomas being the most frequent.
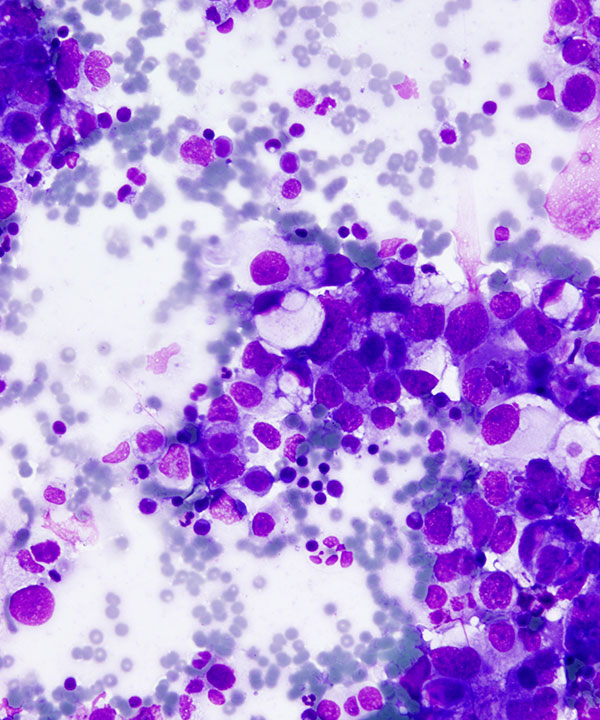
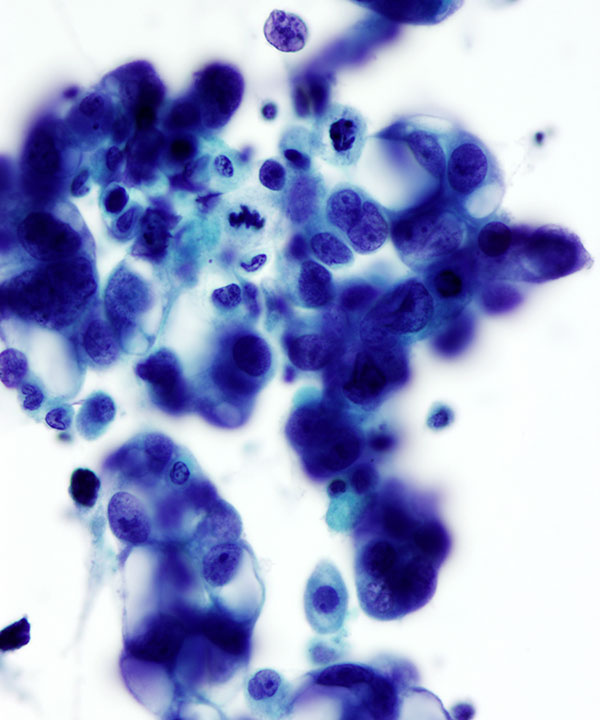
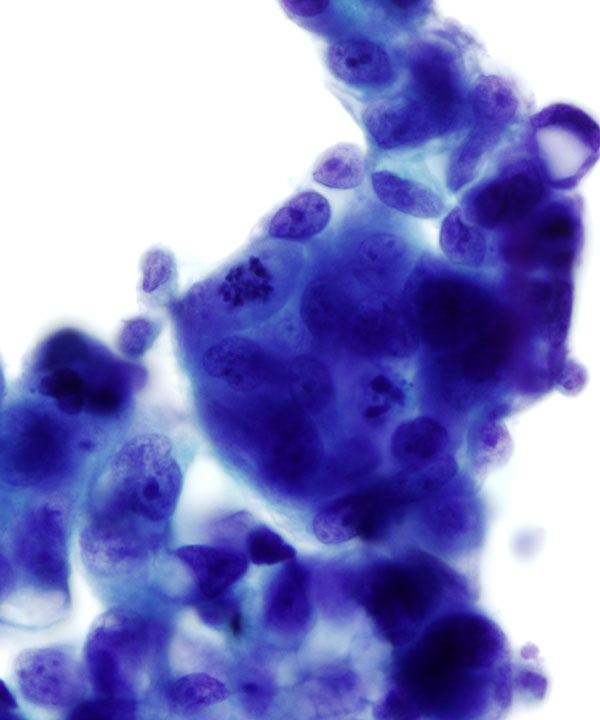
• Foreign population of cells that stand out from mesothelial cells and histiocytes
• Exception:
- cells that mimic native cells
- all tumor cells so they all look alike
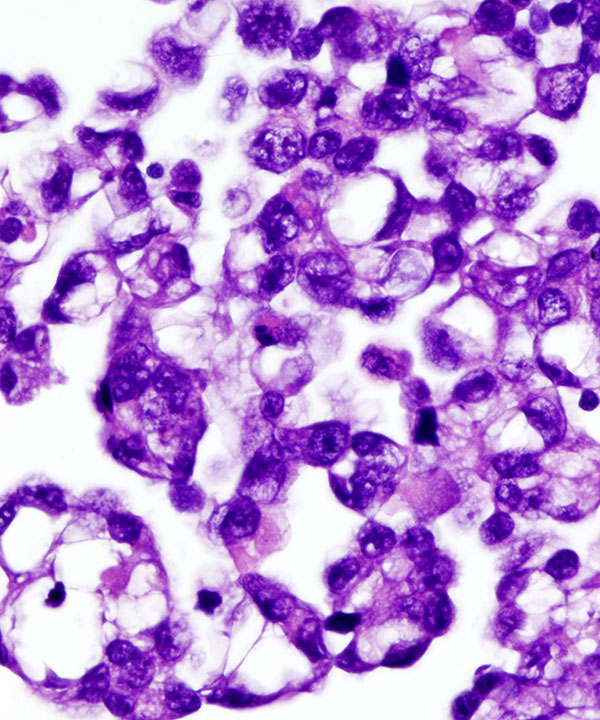
• Carcinomas typically form cohesive clusters and ball up to form spheres with smooth community borders ; however some tumors shed as single cells (lobular breast carcinoma, gastric signet ring cells). May or may not have malignant features (enlarged irregular nuclei with pleomorphism) but usually have high N:C ratios and coarse chromatin.
• Single cells with signet ring morphology
• May have 3D clusters
• Cytoplasmic mucin pushing nucleus forming signet ring
• Nucleus pushed to periphery
• Classically indented nucleus, may be round
• Chromatin fine
• Prominent nucleoli
• IHC: Tumor cells typically express cytokeratin , MOC31, BerEP4, while negative for calretinin (D/D mesothelial cells) and CD68 or CD163 (histiocytes)