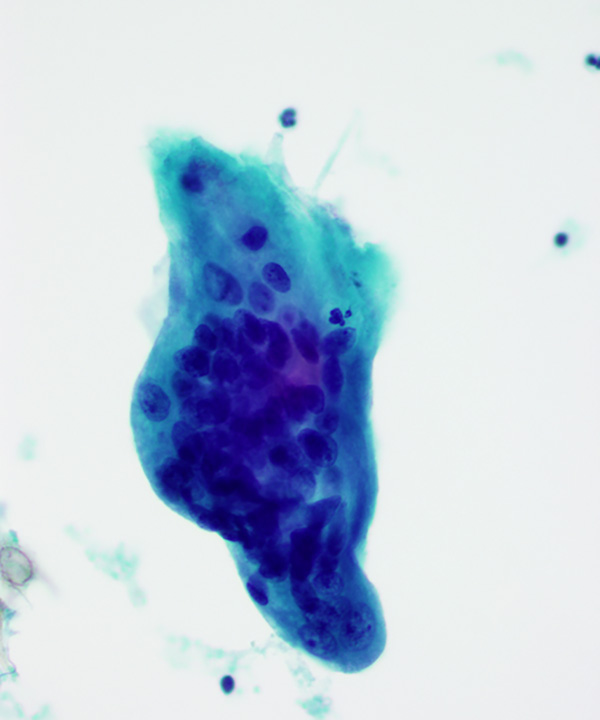
Features
• Also known as calcifying epithelioma of Malherbe
• Most commonly found in head/neck and upper extremities
• Majority seen in children/teenagers
• Pitfall: Squamous cell carcinoma, make sure the clinical and radiographic information correlates
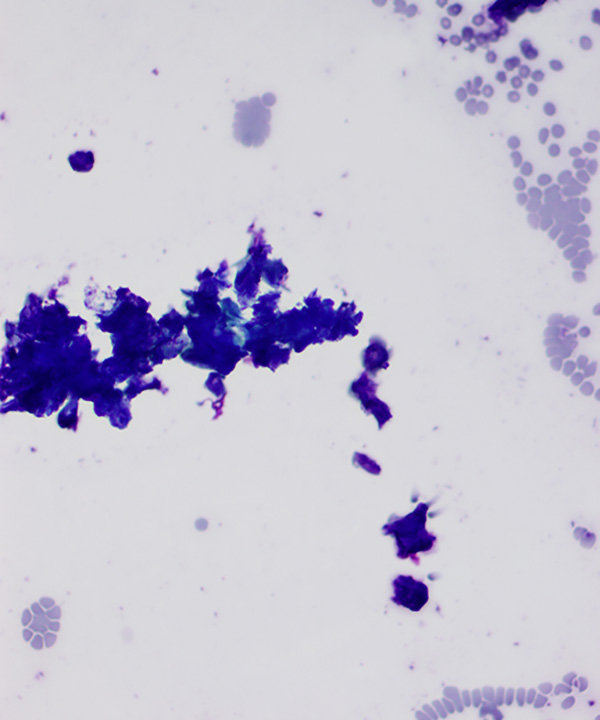
• Typically cellular
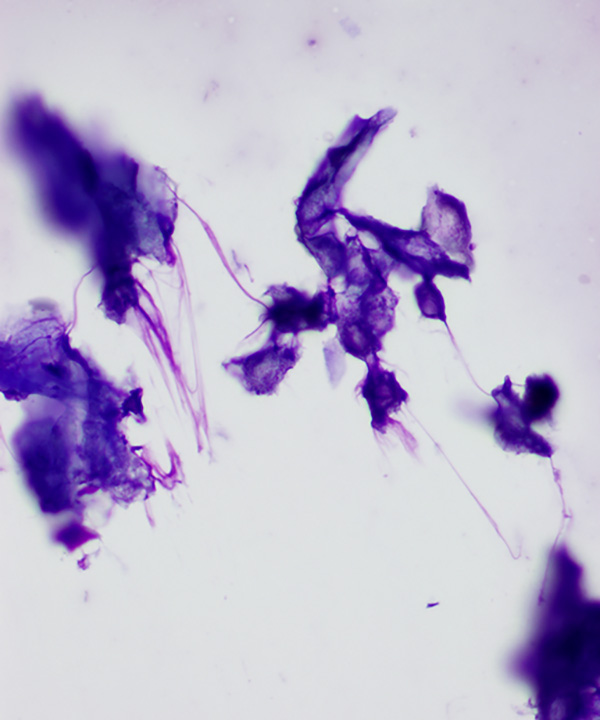
• Cohesive fragments of basaloid type cells and clumps of keratin
• Basaloid cells with relatively high nuclear to cytoplasmic ratios
• Keratin debris
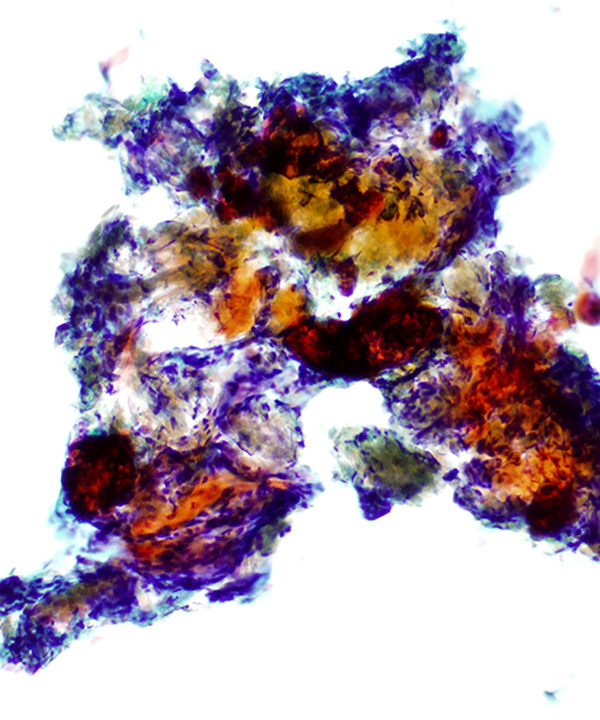
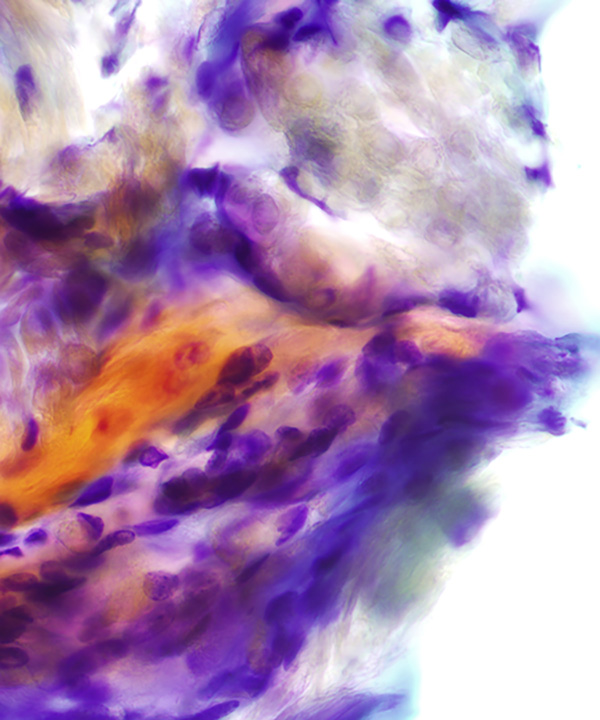
• Ghost cells (eosinophilic cells devoid of nuclear staining)
• Multinucleated giant cells commonly seen
• Nucelar contours are typically smooth
• Chromatin is evenly dispersed
• Nucleoli visible to prominent
• Ghost cells: lack nuclear staining
• Clumps of keratin debris
• May have calcification and metaplastic bone
• Lemos MM et al: Fine-needle aspiration features of pilomatrixoma. Cancer. 93(4):252-6, 2001
• Ieni A et al: Limits of fine-needle aspiration cytology in diagnosing pilomatrixoma: a series of 25 cases with clinico-pathologic correlations. Indian J Dermatol. 57(2):152-5, 2012