Features
• Pure mucinous carcinoma is rare (<2%)
• Often occurs in postmenopausal women
• Has favorable prognosis
• Well-circumscribed with soft gelatinous consistency
• More commonly seen as mixed component with ductal carcinoma
• FNA typically cannot exclude ductal component, so mucinous carcinoma is usually not a FNA diagnosis
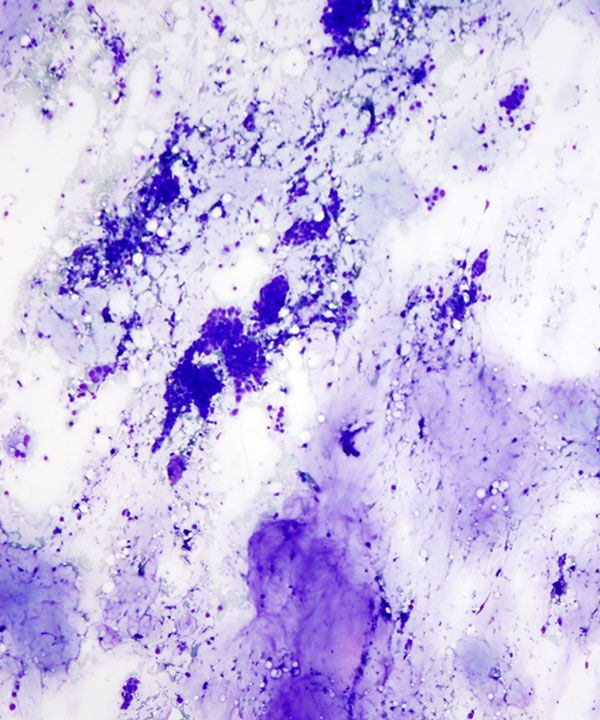
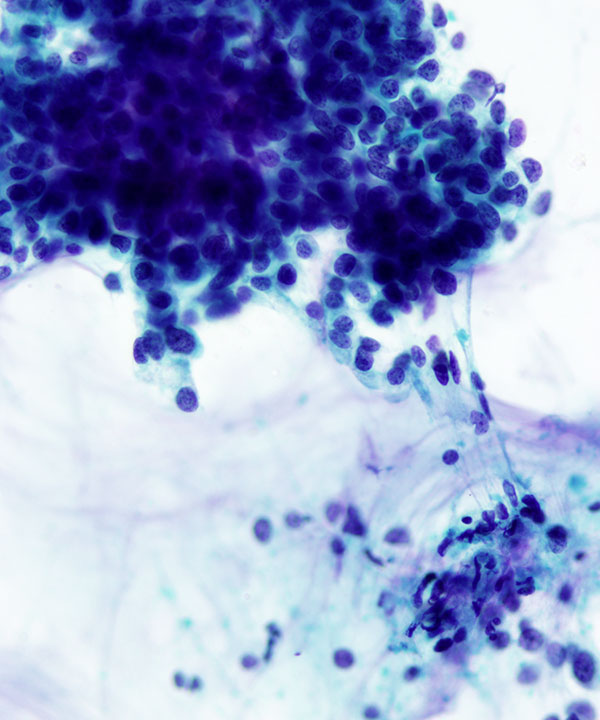
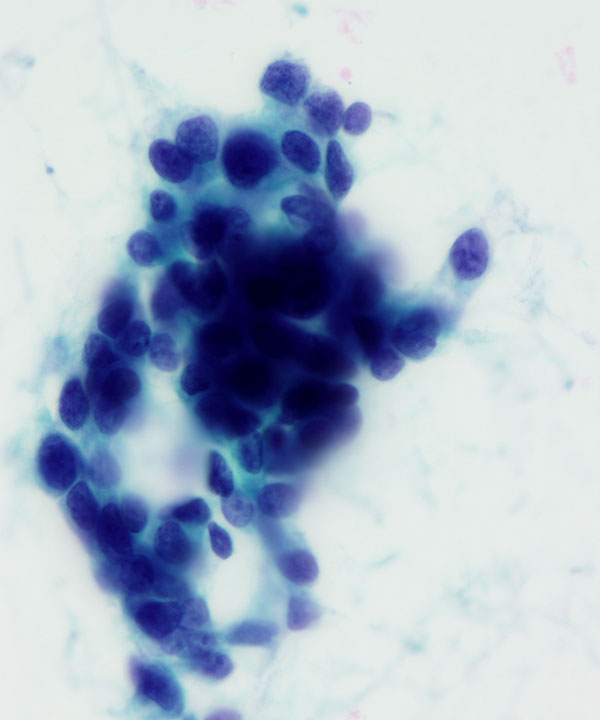
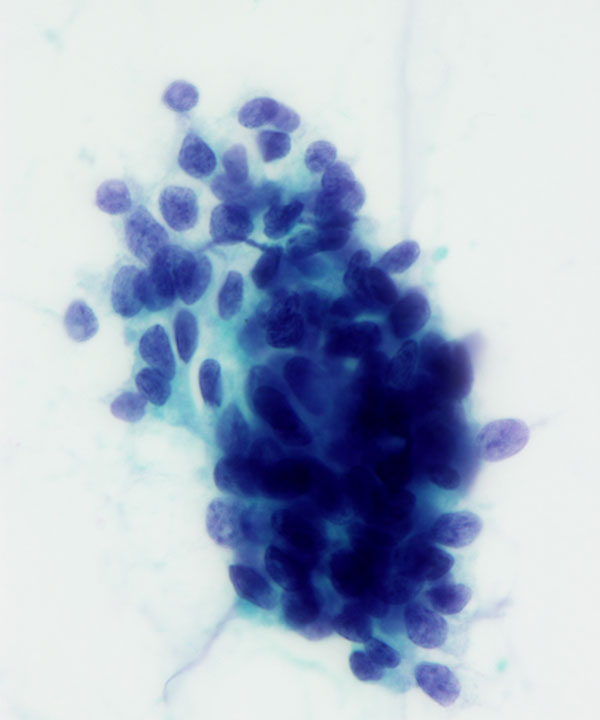
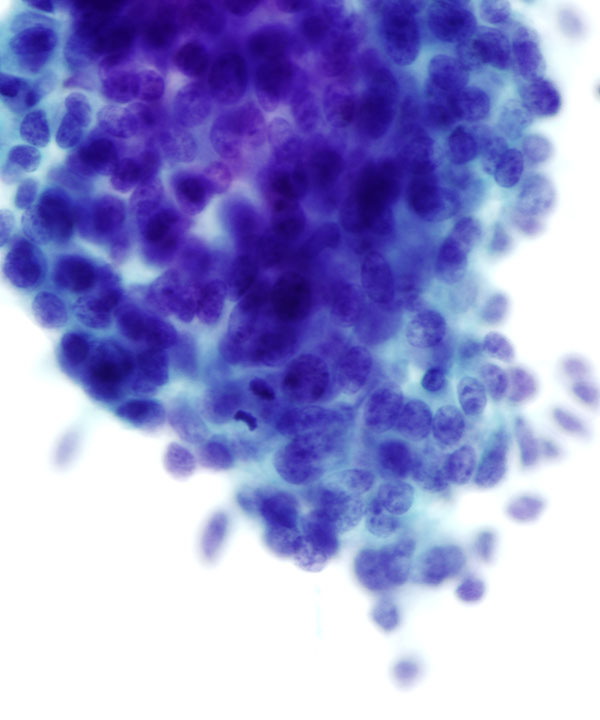
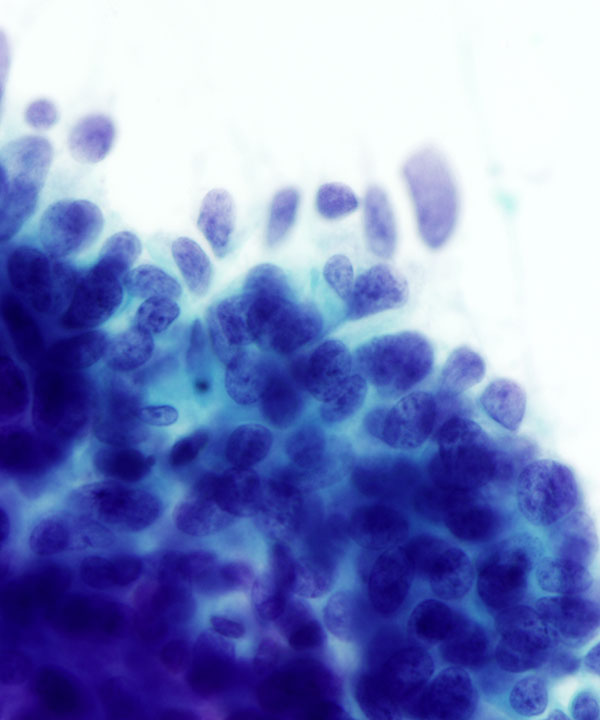
• Cellular smears
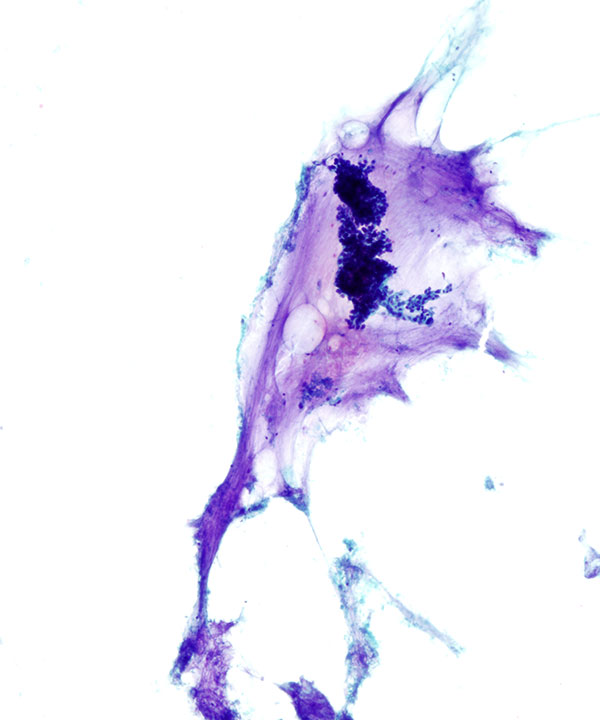
• Nests of tumor cells floating in mucin
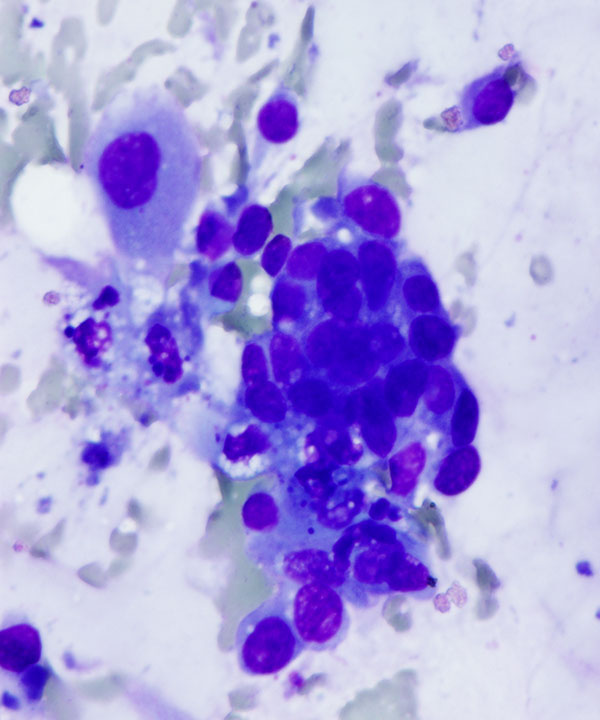
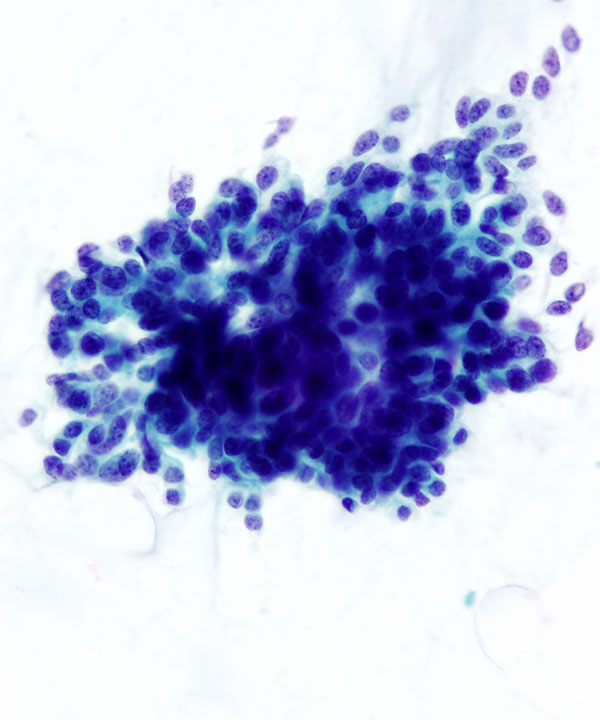
• 3D clusters, sheets, single cells
• Bland uniform cells
• May have mild atypia
• Intracellular cytoplasmic mucin vacuoles
• May have neuroendocrine differentiation
• Round to oval, uniform nuclei
• May have eccentric nuclei
• Fine chromatin
• Small inconspicuous nucleoli
• Abundant extracellular mucin
• Necrosis/mitosis rare
• No myoepithlial cells
• May have branching vessels
• Duane, GB et al. Acta Cytol. 1987 Nov-Dec;31(6):742-50.