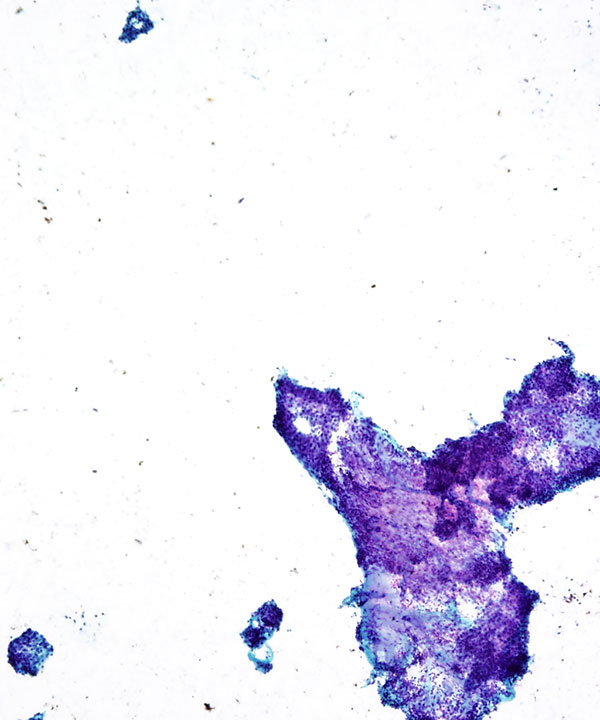
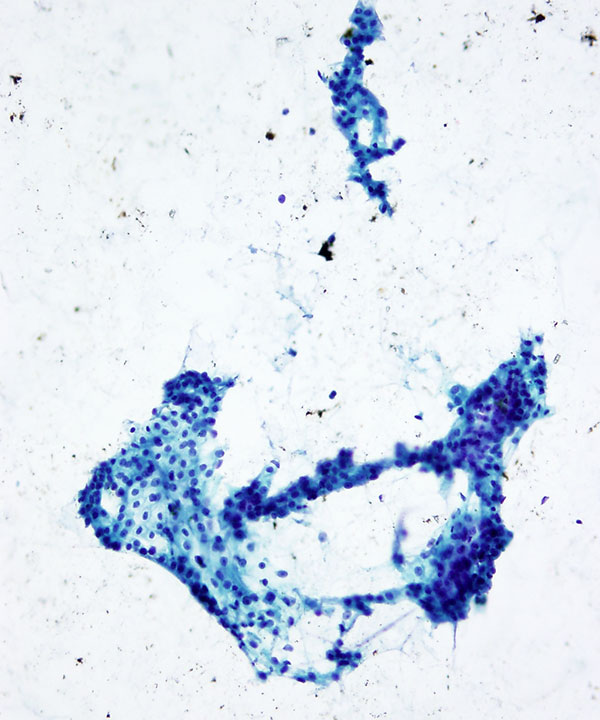
Features
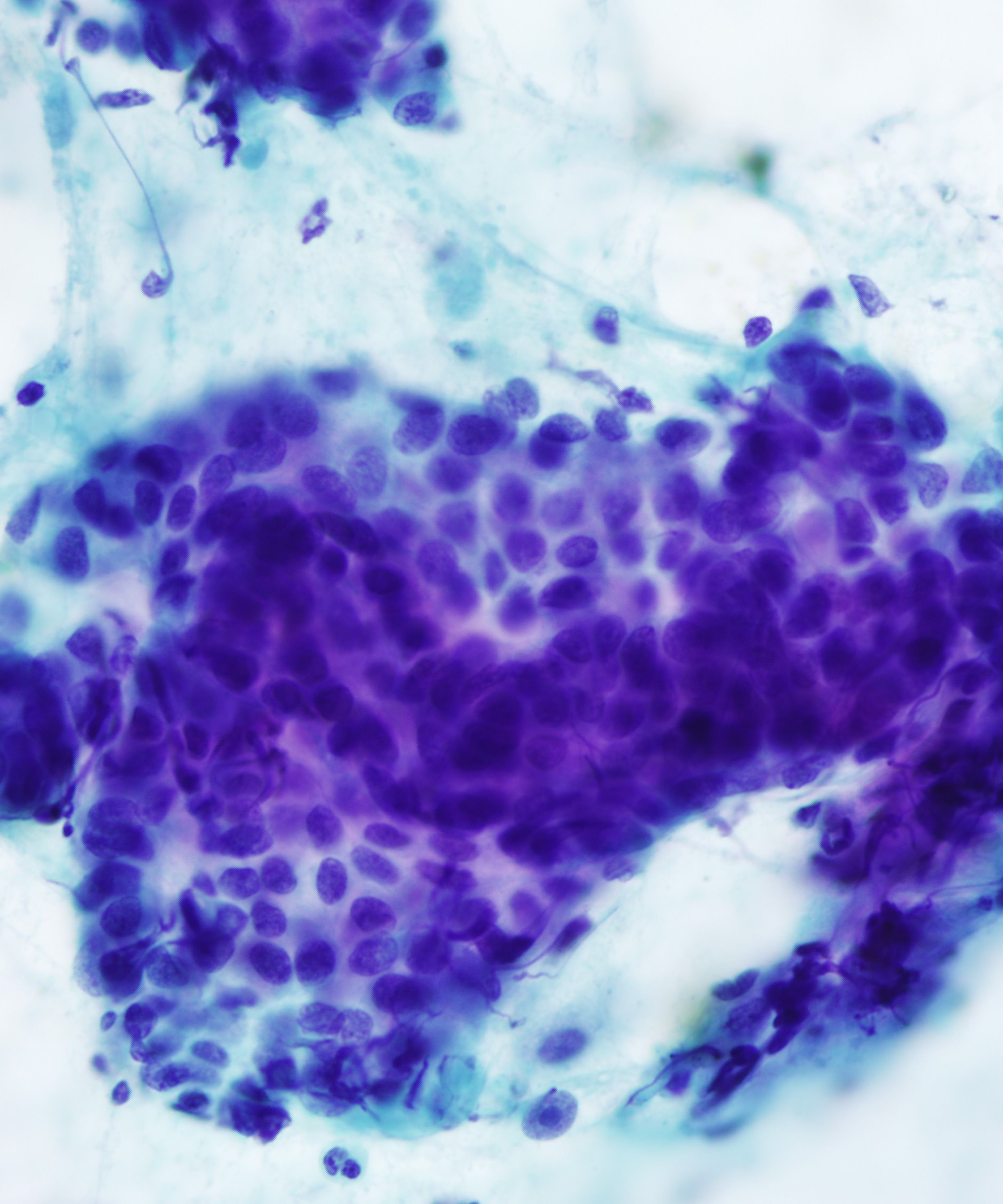
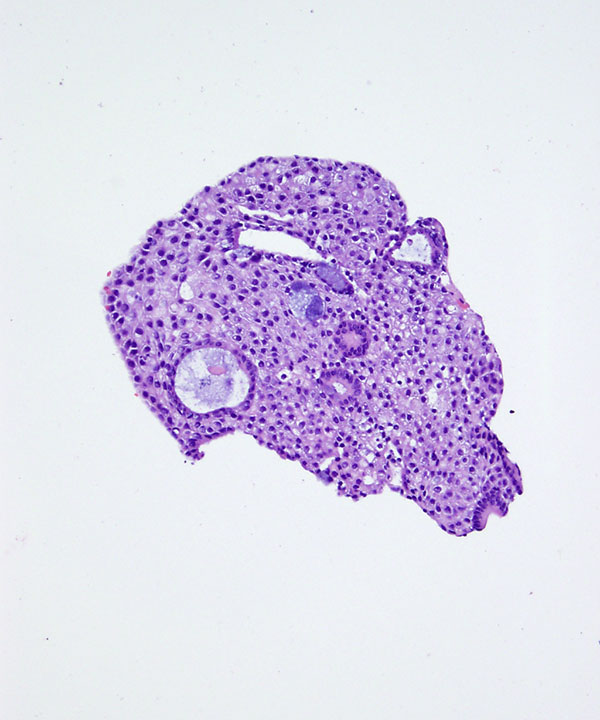
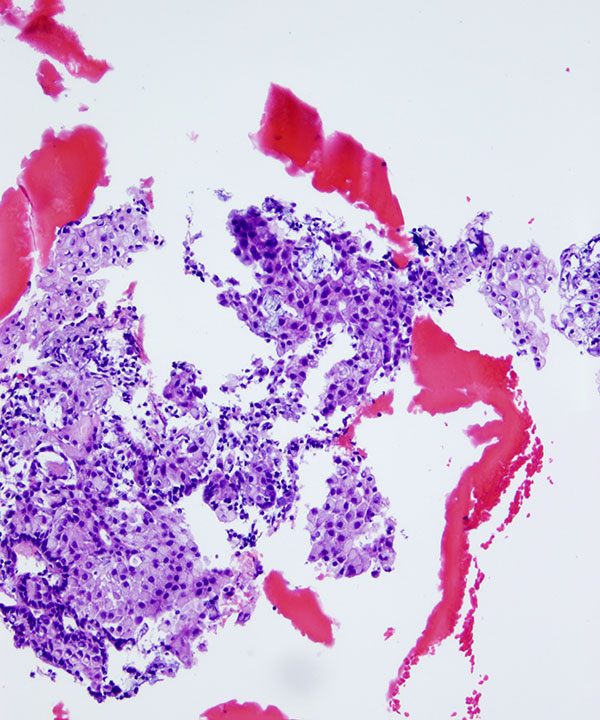
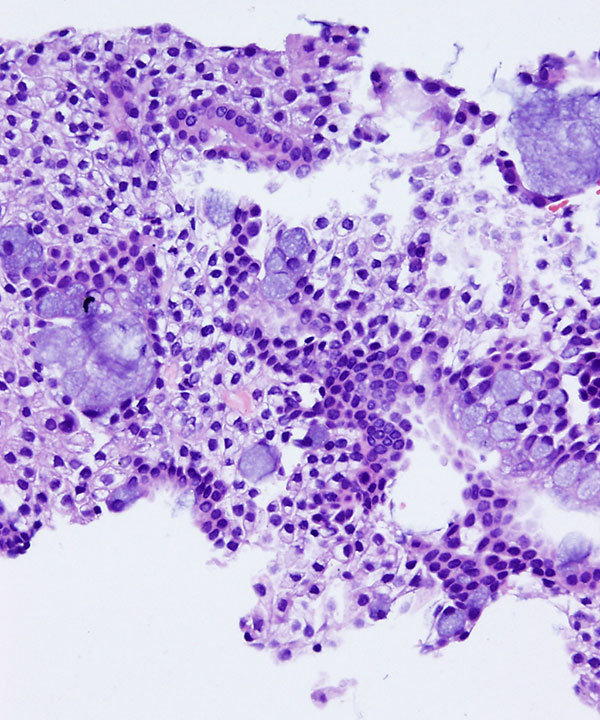
• Cellular smear with mixed cell types
– Glandular
– Squamous
– Intermediate cells
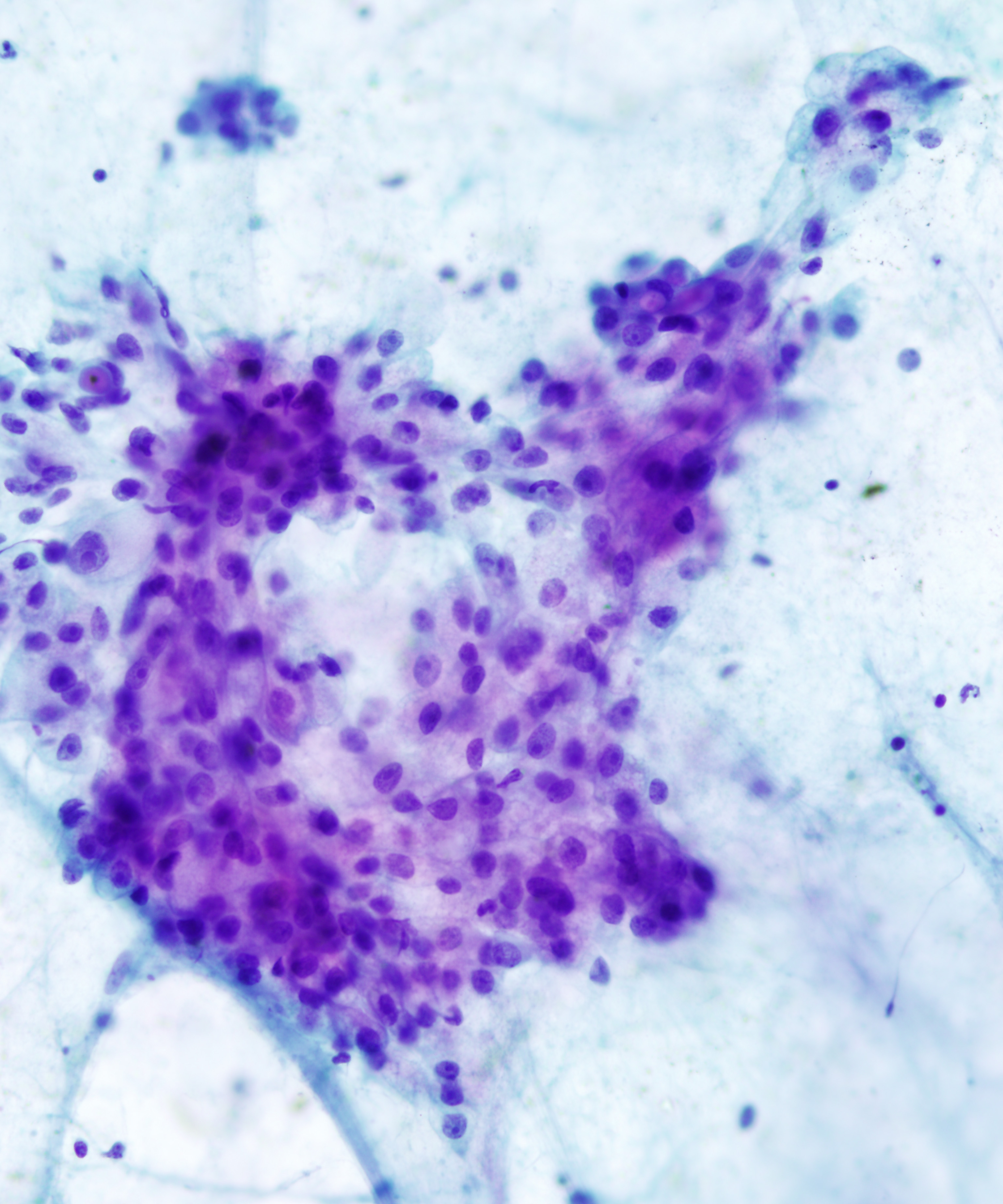
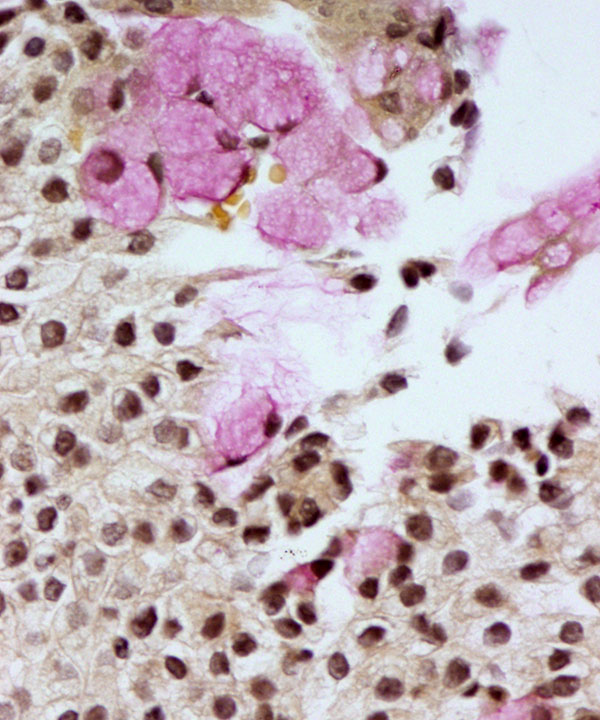
• Mucus/glandular cells
– Round to columnar with abundant vacuolated cytoplasm
– Cytoplasm contains mucin vacuoles
– Cells may be embedded in mucin
• Intermediate cells
– Small cells with high N:C ratios
– Similar to ductal cells
– Scant well defined cytoplasm
– Can differentiate to mucus cell or squamous cell
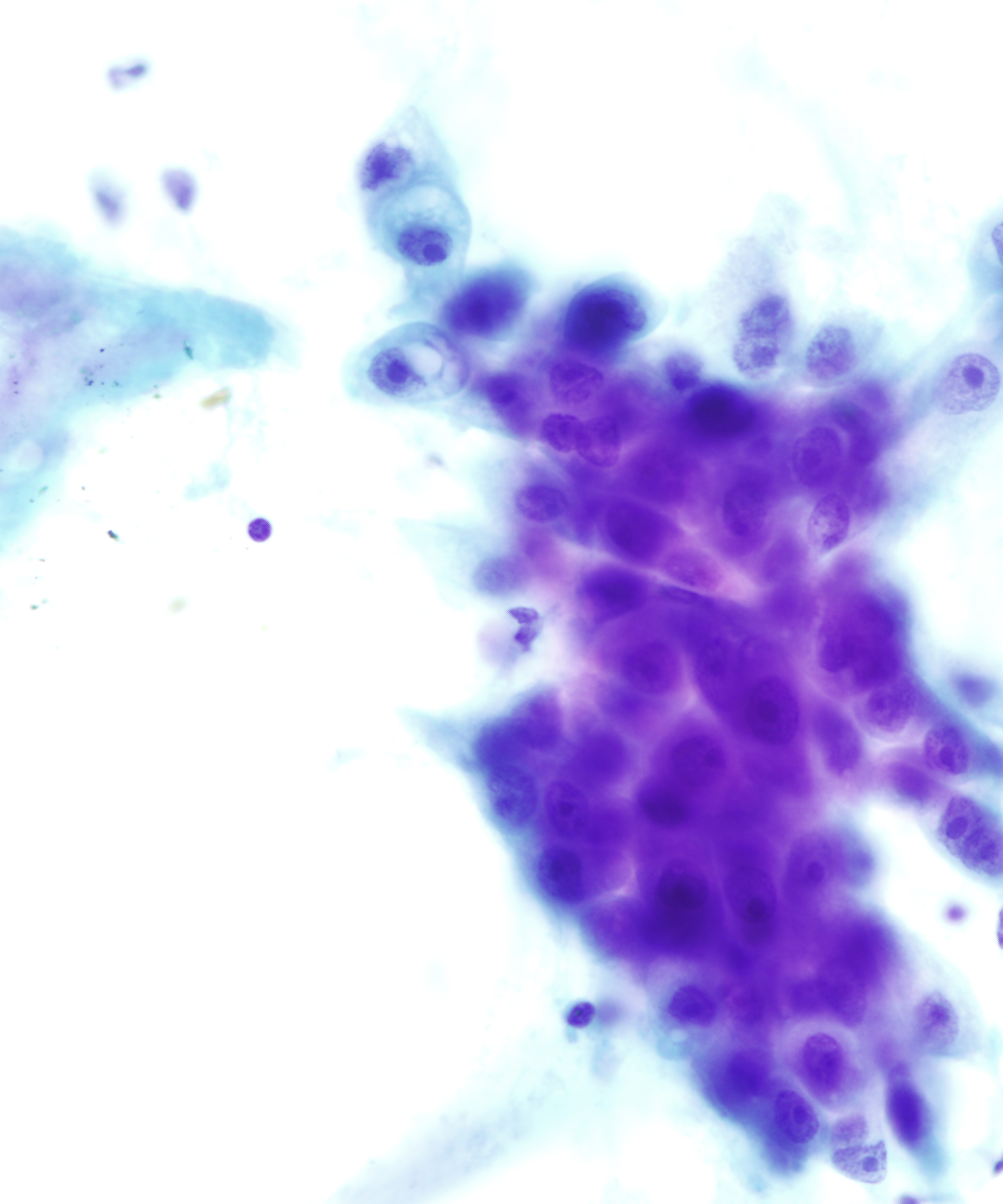
• Squamous cells
– Immature parabasal-like cells with scant dense cytoplasm
– Mature superficial-like cells with abundant thin cytoplasm
• Glandular cells have small round often bland nuclei
• Intermediate cells with round central nuclei, vesicular chromatin and small nucleoli
• Squamous cells : nuclei can be pyknotic
• Nuclear features vary with grade
• Higher grade MEC have irregular enlarged nuclei, clumped chromatin, prominent nucleoli
• Mucin usually present
• May have inflammation
• Low grade tumors usually soft and cystic while high grade tumors are firm and solid. Low grade MEC have abundant mucoid material and predominantly well-differentiated mucus cells; background is cystic (metachromatic on DQ). High grade MEC typically contain squamous and intermediate cells with malignant features, mucous cells can be hard to identify.
• Express cytokeratin, vimentin, S100, actin, AFP, CEA. High Ki-67 and high MUC1 associated with high grade carcinoma. MUC4 assciated with low grade carcinoma.
• Translocation t(11;19) MECT1:MAML2 fusion may be present
Zajicek J et al. Acta Cytol. 1976 Jan-Feb;20(1):35-41.
Kumar N et al. Acta Cytol. 1991 May-Jun;35(3):357-9.